Running a business can be incredibly rewarding, but it also comes with its share of challenges. If your company is struggling with debt, you’re not alone. Many businesses face financial difficulties, especially in uncertain economic times. The good news? You have options beyond simply closing your doors. Business debt restructuring can be your strategic path to resilience, a way to breathe new life into your company and protect your hard-earned legacy. It’s about saving what you’ve built and giving your business a crucial second chance.
At Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc., we understand the stress and uncertainty that business debt can bring. We are Licensed Insolvency Trustees in Ontario, and our purpose is to help Canadian businesses like yours find real, lasting solutions. We pride ourselves on providing clear, actionable, and empathetic advice. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about business debt restructuring, from understanding your options to rebuilding for future success.
Business Debt Restructuring Key Takeaways
- Business debt restructuring allows your company to reorganize its debts, often reducing the total amount owed or extending repayment terms, or both, to avoid bankruptcy.
- Acting early when warning signs appear is crucial to having the most options and a higher chance of success for your business.
- In Canada, options range from informal talks with creditors to formal processes like Division 1 Proposals (BIA) and CCAA Plans of Arrangement, each suited for different business sizes and debt levels.
- A Licensed Insolvency Trustee (LIT) is your indispensable guide through this complex process, offering expert, unbiased advice and legal authority to administer formal restructuring plans.
- Restructuring aims for growth and survival, helping you rebuild financial health, restore trust, preserve jobs, and create a stronger foundation for a thriving future.

business debt restructuring
1. What is Business Debt Restructuring? A Strategic Path to Resilience
Business debt restructuring is a way for companies facing financial trouble to reorganize what they owe. It’s a strategic move to help your business stay afloat, recover, and avoid bankruptcy. Instead of giving up, you work with your creditors to create a new, more manageable payment plan. This process is designed to give your company a fresh start, allowing it to focus on its core operations and return to profitability.
1.1 Defining Business Debt Restructuring
Simply put, business debt restructuring involves changing the terms of your company’s existing debts. This can mean reducing the total amount you owe, extending the time you have to pay it back, or a combination of both. It might also involve lowering interest rates or changing the type of debt. The main goal is to make your debts manageable so your business can continue to operate and eventually thrive. It’s about finding a constructive solution for long-term economic stability and preventing a business failure.
For many Ontario businesses, this means finding a way to lower their monthly debt payments so that cash flow can be directed back into operations. It’s a proactive measure that focuses on keeping your business alive and well, rather than letting debt lead to closure. As Licensed Insolvency Trustees, we at Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc. specialize in helping you define and execute the most effective restructuring strategy.
1.2 Why Businesses Face Financial Difficulties
Many factors can lead a business into debt. Understanding these causes is often the first step in finding a solution. These might include:
- Slow Sales: A sudden or prolonged drop in how much you sell can quickly impact your income.
- High Operating Costs: Expenses like rent, supplies, wages, and utilities can become too high, making it difficult to generate a profit.
- Economic Downturns: Times when the economy is generally weak, or specific industries are struggling, can reduce customer spending and business opportunities.
- Unexpected Events: Major unforeseen events, such as a pandemic, natural disaster, or a significant disruption in your industry (e.g., new technology, increased competition), can severely impact revenue.
- Poor Cash Flow Management: Even profitable businesses can struggle if they don’t have enough money coming in at the right time to cover daily expenses. This is often a symptom, not the root cause.
- Over-reliance on Debt: Borrowing too much to fund operations or growth, especially if the new ventures don’t generate expected returns, can quickly lead to an unmanageable debt load.
- Poor Management Decisions: Strategic errors, ineffective marketing, or expansion at the wrong time can contribute to financial distress.
Identifying the root cause of your business’s financial problems is a key part of the assessment process we conduct at Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc.
1.3 Identifying Early Warning Signs of Financial Distress
Recognizing problems early is key. Waiting too long limits your options significantly and increases the severity of the situation. The earlier you act, the more choices you’ll have to save your business. Look out for these critical signs:
- Difficulty Paying Bills Consistently: You’re regularly late paying suppliers, employees, or taxes (like HST or payroll remittances to the CRA).
- Defaulting on Loans: Missing payments or breaking terms with your bank or other lenders.
- Relying on Personal Funds: You or all the owners are using personal money, credit cards, or lines of credit to keep the business going. This blurs the line between personal and business finances and is a major red flag.
- Reduced Profits or Sustained Losses: Your business is consistently making less money, or even losing money, over several financial periods.
- Chronic Cash Flow Issues: Not having enough liquid cash to meet immediate operational needs, even if you’re making sales on paper. This can lead to a reliance on short-term, high-interest borrowing.
- Increased Creditor Calls or Letters: You’re receiving more frequent and urgent demands for payment from creditors, often accompanied by threats of legal action.
- Lost Supplier Credit: Suppliers demand cash on delivery because they no longer trust your ability to pay.
If you recognize any of these signs, it’s a strong indication that it’s time to seek professional advice. Contacting Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc. at this stage can open up a wider range of solutions for your company.
1.4 The Strategic Advantage: Restructuring for Growth, Not Just Survival
Business debt restructuring isn’t just about surviving; it’s about setting your business up for future success. It provides much-needed “breathing room” from relentless creditor pressure, allowing you to refocus your energy on running and improving your operations. By dealing with debt strategically, you can:
- Stabilize Your Finances: Achieve a manageable debt load and improve cash flow.
- Preserve Jobs: Keep your employees working and contribute to the local economy.
- Maintain Your Business Reputation: Avoid the stigma and damage of bankruptcy.
- Protect Personal Guarantees: Reduce the risk to your personal assets if you’ve personally guaranteed business debts.
- Create a Stronger Foundation for Growth: Once the debt burden is lifted or reduced, your business can invest in expansion, innovation, and profitability.
This proactive approach, guided by experts like Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc., can transform a challenging situation into a powerful opportunity for renewal and sustained growth.
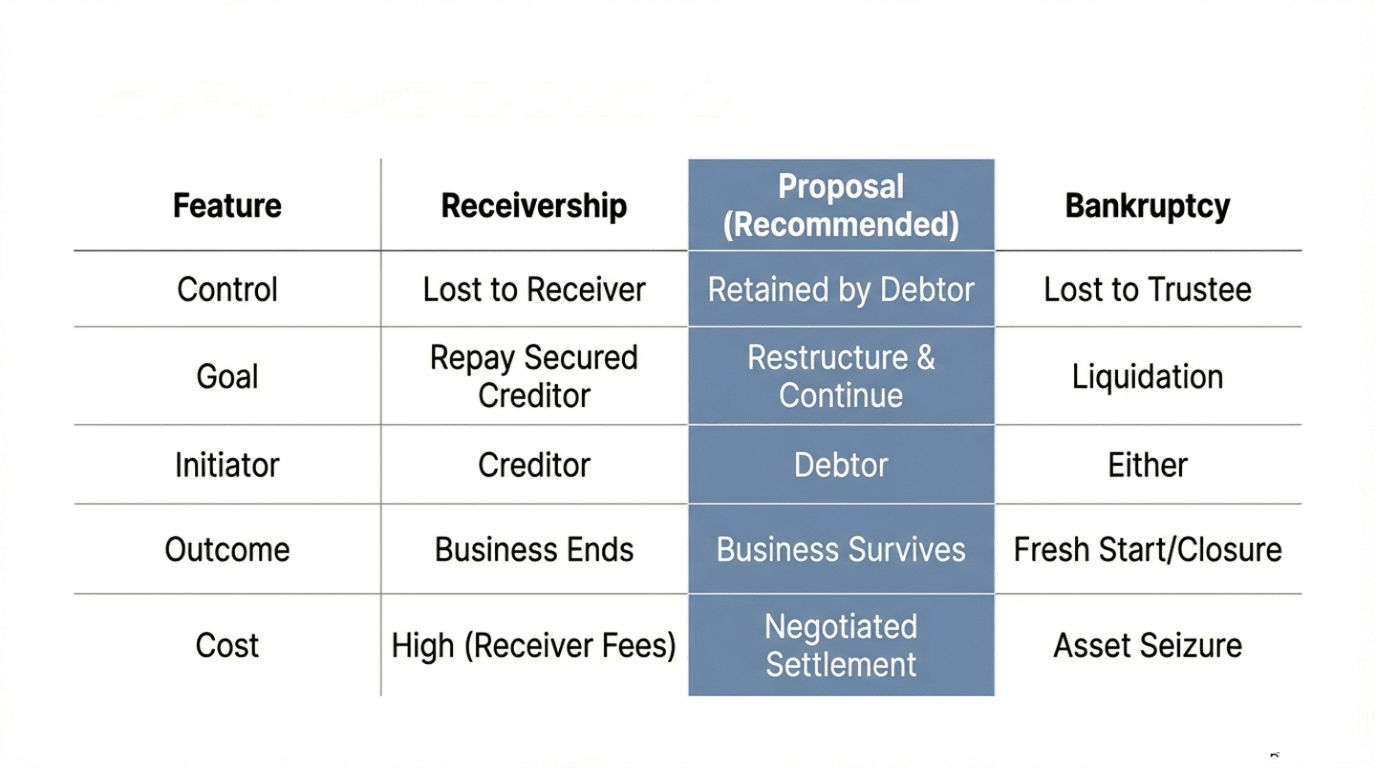
2. Navigating the Landscape of Business Debt Restructuring Options
In Canada, businesses have several options for business debt restructuring. These generally fall into two categories: informal (out-of-court) and formal (court-supervised) processes. The right choice depends on your specific situation, how much debt you have, the number and type of creditors, and the willingness of your creditors to cooperate. Understanding these options is crucial, and an experienced Licensed Insolvency Trustee can help you weigh the pros and cons of each.
2.1 Informal / Out-of-Court Restructuring Strategies
Informal restructuring means you negotiate directly with your creditors without involving the courts. This approach offers flexibility, efficiency, and privacy, but it requires the voluntary agreement of each creditor.
- Direct Negotiation with Creditors: You can talk directly to banks, suppliers, landlords, and other lenders to ask for new payment terms. This might involve requesting lower interest rates, extending payment periods, pausing payments temporarily (a “payment holiday”), or even a partial forgiveness of debt (a “haircut”). Success depends heavily on your negotiation skills and your creditors’ willingness to cooperate.
- Debt Consolidation: Combining multiple smaller debts into one new loan. This often results in a single, lower monthly payment and potentially a lower overall interest rate. However, you need to qualify for the new loan, which can be challenging for a struggling business.
- Refinancing Existing Loans: Securing a new loan to pay off one or more old ones, usually with better terms like a lower interest rate, a longer repayment period, or different collateral requirements. This is viable if your business’s creditworthiness is still reasonably good.
- Forbearance Agreements: Your creditors might agree to temporarily pause or reduce payments, giving your business critical time to recover and improve its financial position. These are short-term solutions, but can be lifesavers.
- Strategic Asset Sales: Selling non-essential company assets (e.g., unused equipment, excess inventory, non-core property) to generate cash. This cash can then be used to pay down specific debts, particularly high-interest ones.
Pros of Informal Restructuring: It’s generally less costly, faster to implement if agreements are reached, and keeps the process private. It also maintains direct control over your business decisions. Cons of Informal Restructuring: Creditors are not obligated to agree to new terms. A single dissenting creditor can derail the entire process, and there’s no legal protection from collection actions if an agreement isn’t reached.
2.2 Formal / Court-Supervised Restructuring Processes
Formal restructuring options involve the court system and provide legal protection from creditors. These are generally used when informal talks fail, when there are many creditors, or when the debt is too large and complex to manage through private negotiations. In Canada, the main federal laws governing corporate insolvency are the Bankruptcy and Insolvency Act (BIA) and the Companies’ Creditors Arrangement Act (CCAA). A Licensed Insolvency Trustee (LIT) plays a central and legally mandated role in these processes.
- Division 1 Proposal (under the BIA): This is a formal, legally binding offer made by an insolvent company to its creditors to settle its debts. It’s often used by small to medium-sized businesses and offers a structured path to debt relief. A Licensed Insolvency Trustee (LIT) helps prepare the proposal, files the necessary documents with the Superintendent of Bankruptcy, and oversees the entire process. Filing a proposal immediately creates a “stay of proceedings,” which is a legal order that stops creditors from taking further legal action, like lawsuits, garnishments, or seizure of assets. If approved by the majority of creditors (by number and 2/3 by value of those voting) and the court, all unsecured creditors are legally bound by the terms of the proposal, even if they voted against it. This provides a powerful collective solution.
- Companies’ Creditors Arrangement Act (CCAA): The CCAA is designed for larger, more complex corporations with debts over $5 million. It offers a very flexible, court-supervised process to reorganize a company’s affairs and avoid bankruptcy. Like a BIA proposal, it provides an immediate and comprehensive stay of proceedings, giving the company valuable time to develop a comprehensive plan of arrangement. A court-appointed Monitor (who is always a Licensed Insolvency Trustee) oversees the company’s financial activities and reports to the court during the process. The CCAA is particularly useful for complex corporate structures or when there are multiple secured creditors and significant intercompany debts.
The team at Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc. has extensive experience with both BIA Proposals and CCAA filings, guiding businesses of all sizes through these intricate legal frameworks to achieve successful outcomes.
Comparison Table: Informal vs. Formal Business Debt Restructuring in Canada
Feature | Informal / Out-of-Court Restructuring | Formal / Court-Supervised Restructuring (BIA Proposal or CCAA) |
|---|---|---|
Legal Protection | No automatic legal protection from creditors. | Automatic “stay of proceedings” legally stops most creditor actions (e.g., lawsuits, collections, asset seizures). |
Creditor Consent | Requires voluntary agreement from each individual creditor. | Once approved by a majority of creditors (voting) and the court, it is legally binding on all included creditors, even those who disagreed. |
Cost | Generally lower (may involve legal/financial advisor fees). | Generally higher due to court and professional fees (e.g., LIT fees, legal fees, Monitor fees). |
Timeframe | Can be quicker if all parties agree; no set legal timeline. | Structured timelines; can be longer due to court procedures and creditor meetings. BIA Proposals typically conclude in several months, CCAA can take longer. |
Public Record | Private and confidential. | Public record, as court filings are involved (though details may be limited). |
Eligibility | Any business; depends heavily on the willingness and cooperation of creditors. | BIA Proposal: Any insolvent company, often smaller to mid-sized businesses. CCAA: Corporations with debts typically exceeding $5 million. |
Oversight | Debtor manages negotiations directly. | Supervised by a Licensed Insolvency Trustee (for BIA Proposal) or a court-appointed Monitor (for CCAA). |
Risk of Bankruptcy | Higher if creditors don’t cooperate; no legal shield. | Filing a BIA Proposal can lead to automatic bankruptcy if rejected by creditors or the court. CCAA rejection does not automatically lead to bankruptcy, allowing more flexibility. |

3. The Step-by-Step Business Debt Restructuring Process
Navigating business debt restructuring can seem overwhelming, but with the right guidance from a professional, it’s a clear and manageable process. Here’s how it generally works, highlighting the key stages your business will go through with the support of a Licensed Insolvency Trustee.
3.1 Initial Financial Assessment: Understanding Your Situation
The first critical step is to get a clear, honest, and comprehensive picture of your company’s financial health. This involves:
- Reviewing All Debts: Creating a detailed list of every creditor, the exact amount owed to each, interest rates, repayment terms, and whether the debt is secured or unsecured.
- Analyzing Cash Flow: Thoroughly understanding how much money consistently comes into and goes out of your business on a monthly or quarterly basis. This helps identify shortfalls and potential areas for improvement.
- Evaluating Assets: Listing everything your company owns, including real property, equipment, inventory, accounts receivable, and intellectual property. This helps determine what assets might be available to leverage or sell.
- Identifying Root Causes: Pinpointing why your business is in financial distress. Is it a temporary blip, or are there deeper, systemic issues?
- Operational Review: Looking at your business model, products, services, and market position to identify strengths and weaknesses.
This detailed assessment, which is a core service provided by Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc., helps determine if restructuring is the right path and which specific options are best suited for your unique circumstances. It also provides the essential information that creditors will need to evaluate any proposed plan.
3.2 Developing a Robust Restructuring Plan
Once you fully understand your situation, you’ll work with your advisors, especially your Licensed Insolvency Trustee, to create a detailed plan. This plan outlines precisely how you propose to deal with your debts. A well-crafted plan is realistic, addresses the root causes of financial distress, and offers creditors a better outcome than if your business were to go bankrupt. It might include:
- New Payment Schedules: Proposing lower monthly payments, extending repayment periods, or even a temporary payment holiday.
- Debt Reduction: Offering to pay a portion of the original debt, often a percentage that creditors accept because it’s more than they’d get in a bankruptcy.
- Operational Changes: Outlining specific ideas for how the business will improve profitability, cut unnecessary costs, increase revenue, or streamline operations to support the new debt plan.
- Cash Flow Projections: Providing clear, forward-looking financial statements that demonstrate how your business will generate enough money to meet the new debt obligations.
- Asset Management: Details on any proposed asset sales or how secured assets will be managed.
At Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc., we guide you through this complex planning phase, ensuring your proposal is comprehensive, credible, and legally sound.
3.3 Engaging with Creditors: The Art of Negotiation
This is the stage where the plan is presented to your creditors. Whether informal or formal, negotiation is key, and the role of a professional advisor is crucial.
- Informal: This involves direct, often one-on-one discussions with each creditor. You present your situation and proposal, hoping to gain individual agreement.
- Formal: In a BIA Division 1 Proposal or CCAA filing, your Licensed Insolvency Trustee acts as the official intermediary and negotiator. They prepare the formal proposal, send it to all creditors, and manage all communications. They will convene a meeting of creditors where they can ask questions and then vote on the proposal. For a BIA Proposal, a proposal is legally accepted if a majority in number and two-thirds in value of those voting agree to it.
Transparency, clear communication, and a well-reasoned, fair plan are crucial for successful negotiations. Our team at Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc. brings years of experience in negotiating with all types of creditors, from major banks to the Canada Revenue Agency, to ensure the best possible outcome for your business.
3.4 Implementing and Monitoring the Restructuring Plan
Once a plan is approved by your creditors and, if necessary, the court, it’s time to put it into action. This phase requires discipline and ongoing vigilance.
- Adhering to New Terms: Making all payments exactly as agreed upon in the restructured plan. This is vital for rebuilding trust and creditworthiness.
- Implementing Operational Changes: Putting into practice any changes identified in your plan to improve business performance, such as cost-cutting measures, new marketing strategies, or improved inventory management.
- Ongoing Monitoring: A Licensed Insolvency Trustee, or a court-appointed Monitor in a CCAA filing, will oversee your company’s progress and ensure the plan is followed. They will review financial reports and report on any significant changes or challenges, ensuring compliance with the terms of the proposal.
3.5 The Indispensable Role of Professional Advisors
Attempting business debt restructuring alone can be extremely difficult, time-consuming, and often leads to missed opportunities or costly mistakes. Professional advisors are crucial for navigating the legal complexities and ensuring a successful outcome.
- Licensed Insolvency Trustees (LITs): In Canada, LITs are the only professionals legally authorized to administer formal insolvency processes like BIA Proposals and CCAA proceedings. They are regulated by the federal government and must provide unbiased advice on all debt options available to your business, not just one. They help you conduct the financial assessment, prepare the restructuring plan, file all necessary documents, manage creditor communication, and oversee the implementation of the plan. Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc. embodies this expertise.
- Legal Counsel: Lawyers can provide specialized advice on corporate law, contracts, specific creditor claims, and represent your business in court if necessary, especially in CCAA cases.
- Accountants/Financial Advisors: Can assist with in-depth financial analysis, forecasting, tax implications of restructuring, and developing operational improvement strategies.
These experts, working together, help you navigate the complexities, protect your interests, and work towards the best possible outcome for your business, allowing you to focus on running your operations.
4. Advanced Strategies and Specific Tools for Debt Relief
Beyond the basic framework, some specific tools and strategies can be part of a comprehensive debt restructuring plan. A skilled Licensed Insolvency Trustee, like those at Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc., can help you determine if these advanced options are suitable for your business.
4.1 Refinancing and Amending Existing Loans
This involves adjusting the terms of current loans or securing new financing to replace old debt. It’s often a central part of both informal and formal restructuring.
- Lower Interest Rates: Negotiating with lenders for reduced interest rates can significantly free up cash flow, making debt more affordable.
- Extended Amortization: Stretching out the repayment period for a loan will lower the required monthly payments, improving immediate cash flow.
- Principal Reductions: In some cases, lenders may agree to reduce the loan principal if they believe it ensures a higher recovery than if the business were to go bankrupt. This is a significant concession and often requires a strong business case.
- Debt Rescheduling: Consolidating multiple loans into one new, more manageable loan with revised terms.
4.2 Debt-for-Equity Swaps for Strategic Restructuring
In a debt-for-equity swap, creditors agree to exchange some or all of the debt they are owed for an ownership stake (equity) in the company. This is a powerful, though often complex, tool.
- Reduces Debt Burden: Immediately lowers the company’s liabilities on its balance sheet, improving its financial health.
- Creditor Buy-in: Creditors become stakeholders and shareholders, motivated by the company’s future success, aligning their interests with the business.
- Common in CCAA: This is a more sophisticated tool often seen in larger restructurings under the CCAA, which allows for addressing shareholder interests and corporate structure changes. It can also be a component of a BIA Proposal in certain circumstances.
4.3 Strategic Asset Sales and Business Debt Reduction
Selling non-essential assets can provide crucial cash to pay down debt, especially for secured creditors.
- Identify Non-Core Assets: Selling equipment, property, or even entire business divisions that are not central to the company’s main operations or future strategy. This helps unlock value from underutilized resources.
- Managed Liquidation: In some cases, a partial or managed liquidation of specific assets can be part of a restructuring to settle particular debts while keeping core operations viable. This is different from a full liquidation in bankruptcy.
- Avoiding Forced Sales: Conducting strategic sales as part of a restructuring allows the business more control over the sale process, potentially achieving better prices than in a forced liquidation.
4.4 Managing Personal Guarantees and Collateral
Many business loans, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises, require personal guarantees from owners or collateral (assets pledged against the loan). This is a critical area where an LIT can help protect you.
- Impact on Personal Assets: If you have personally guaranteed a business loan, your personal assets (like your home or savings) could be at risk if the business defaults. Understanding these risks is paramount.
- Negotiating Release or Reduction: Restructuring can sometimes involve negotiating with creditors to reduce or even release personal guarantees, protecting your personal finances. This is a key benefit an LIT can pursue.
- Collateral: Understanding how secured creditors (those who have a claim on specific assets as collateral) are treated in different restructuring scenarios is vital. An LIT can explain their rights and how a proposal might impact them.
Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc. has extensive experience in structuring plans that address personal guarantees, offering advice on how to best protect both your business and your personal financial well-being.

5. Tailored Approaches for Different Creditor Relationships
Different types of creditors require different strategies. A skilled Licensed Insolvency Trustee understands how to approach each relationship effectively to achieve the best outcome for your business debt restructuring efforts. Navigating these relationships is a core part of what we do at Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc.
5.1 Engaging with Banks and Institutional Lenders
Banks and other institutional lenders often hold significant, secured debt, meaning they have a claim on specific business assets (like property, equipment, or accounts receivable) if you don’t pay.
- Clear Communication: Banks need detailed financial information, a credible assessment of the business’s viability, and a solid, realistic plan to consider restructuring. Transparency is key.
- Security Enforcement: They have legal rights to seize collateral to recover their funds. Therefore, negotiations aim to convince them that the restructuring plan offers them a better recovery than enforcing their security and potentially forcing a bankruptcy.
- Forbearance Agreements: Often, banks will agree to temporary relief, such as pausing interest or principal payments, if they see a viable path to recovery and believe the business can eventually pay them back.
- Restructuring Existing Loans: Negotiating for lower interest rates, extended payment terms, or even a partial write-down of debt to make payments manageable.
5.2 Strategies for Government Agencies (e.g., Canada Revenue Agency)
The Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) is a unique and powerful creditor. Debts like unremitted HST, employee source deductions, and corporate income tax are serious and carry different priorities in insolvency.
- Priority Status: Certain CRA debts, like unremitted employee source deductions, have “super-priority” in insolvency, meaning they must be paid first. Unremitted HST also has a high priority.
- Inclusion in Proposals: Unsecured CRA debts (like corporate income tax owing or penalties), including unremitted HST but not unremitted employee source deductions, can be included in BIA Division 1 Proposals, similar to other unsecured creditors, allowing for their reduction or rescheduling.
- Stopping Collection: Filing a formal proposal (BIA or CCAA) will impose a stay of proceedings on the CRA, stopping collection actions like garnishments or demands to third parties.
- Negotiation: An LIT can often negotiate payment arrangements with the CRA directly or include CRA debt in a formal proposal, which can be critical for the business’s survival.
Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc. has extensive experience negotiating with the CRA and understands their unique requirements and powers, ensuring your business’s plan accounts for government debts properly.
5.3 Managing Vendor and Supplier Relationships
Suppliers are crucial for your ongoing operations. Losing their support due to unpaid invoices can cripple your business.
- Maintaining Trust and Communication: Open and honest communication with key suppliers is paramount. Explaining your situation and your plan can help maintain their confidence.
- Negotiating Payment Plans: For outstanding invoices, you might propose extended payment terms or a structured payment plan.
- Identifying Critical Suppliers: Prioritizing essential suppliers whose continued support is vital for your operations. You might need to make special arrangements with them to ensure continued supply.
- Section 81.1 BIA: Suppliers may have rights to reclaim goods delivered within 30 days if your business files for bankruptcy. In a BIA Proposal or CCAA filing, this right is typically stayed, giving the business time to sort things out.
5.4 Addressing Unsecured Creditors
Unsecured creditors (like credit card companies, trade creditors without collateral, or some service providers) generally have fewer rights than secured creditors in an insolvency.
- Inclusion in Proposals: BIA Division 1 Proposals are primarily designed to deal with unsecured creditors. Once a proposal is approved, these creditors are legally bound by its terms, even if they originally disagreed.
- Negotiating Settlements: Informal settlements might involve offering a lump sum payment or a reduced amount over an agreed period, often less than the original debt, in exchange for full release.
- Collective Approach: Formal proposals offer a collective approach, ensuring all unsecured creditors are treated fairly and equally according to the law.
Our expertise at Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc. ensures that all creditor relationships are managed strategically and respectfully, maximizing the chances of a successful debt restructuring.
6. Post-Restructuring: Building a Foundation for Future Success
Completing a debt restructuring is a major achievement, but it’s also the start of a new, crucial chapter. The goal is not just to get out of debt, but to ensure long-term financial health and resilience. This phase is about implementing sustainable practices and rebuilding confidence.
6.1 Rebuilding Financial Health and Trust
The hard work doesn’t stop once the restructuring plan is approved. This phase is about demonstrating consistent financial responsibility.
- Consistent Payments: Sticking to the restructured payment plan without fail is vital for rebuilding trust with all your creditors. Each on-time payment reinforces your commitment.
- Improved Credit Rating: Over time, demonstrating responsible financial management and adherence to your new debt terms will help improve your company’s credit rating, making future financing easier and more affordable.
- Transparency and Open Communication: Continue to be transparent with lenders and stakeholders about your financial performance. Regular updates, even if not legally required, can strengthen relationships.
6.2 Strategic Operational Refinements for Resilience
The restructuring process often forces a deep, critical look into your business operations. Use this opportunity to make lasting improvements that build resilience.
- Cost Control: Maintain strict control over expenses. Implement ongoing review processes to identify and eliminate unnecessary costs.
- Efficient Operations: Streamline processes, improve productivity, and adopt new technologies to enhance efficiency and profitability. This might involve re-evaluating supply chains or internal workflows.
- Revenue Growth Strategies: Focus on diversifying income streams, improving sales and marketing efforts, and exploring new markets to ensure stable and increasing revenue.
- Contingency Planning: Develop robust plans for unexpected future challenges, including financial reserves and alternative operational strategies.
6.3 Cultivating Sustainable Financial Stability
Long-term success relies on establishing healthy financial habits that prevent a return to financial distress.
- Strong Cash Flow Management: Implement robust systems to manage cash flow effectively. Forecast regularly, monitor receivables and payables closely, and maintain sufficient working capital.
- Prudent Borrowing: Be cautious about taking on new debt. Evaluate every borrowing decision carefully, ensuring it’s for strategic growth and manageable within your cash flow.
- Building Financial Reserves: Create an emergency fund for your business to handle future economic downturns, unexpected expenses, or investment opportunities without immediately resorting to debt.
- Regular Financial Reviews: Continuously monitor your financial performance, compare it against your projections, and adjust strategies as needed. Engage regularly with your accountant and financial advisors.
6.4 The Human Element: Managing Stress and Emotional Impact
Business debt takes a heavy toll on owners, management, and even employees. The process can be emotionally draining.
- Seek Support: Don’t hesitate to seek emotional support from peers, business mentors, or mental health professionals. You don’t have to go through this alone.
- Communicate with Your Team: Be transparent (within appropriate limits) with your employees about the restructuring process and the positive future vision. Their understanding and support are invaluable.
- Focus on the Future: Remind yourself and your team that this challenging period is a step towards a stronger, more stable future for the business.
- Celebrate Milestones: Acknowledge progress and successes along the way, no matter how small. This helps maintain morale and motivation.
The guidance of a compassionate professional, like the Licensed Insolvency Trustees at Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc., can significantly reduce this emotional burden. We support you not just with legal and financial expertise, but also with reassurance and understanding throughout the entire journey.

7. Your Next Steps: Choosing the Right Path to Debt Relief
Facing business debt is tough, but ignoring it only makes things worse. Taking action and doing so early is the most crucial step you can take. Remember, business debt restructuring is a powerful tool to save your company and allow it to thrive again.
7.1 Self-Assessment: Is Restructuring the Right Solution?
Before taking the leap, ask yourself these honest questions:
- Is my business fundamentally viable, meaning its products or services are still in demand, but it’s just burdened by too much debt?
- Do I believe the business can be profitable and sustainable if its debt load is adjusted to a manageable level?
- Am I willing to make necessary operational changes, cut costs, or adjust strategies to ensure the new debt plan succeeds?
- Do I want to protect the jobs my business provides and maintain my legacy?
If you answered yes to these questions, business debt restructuring is likely a viable and preferable alternative to closing your business.
7.2 The Imperative of Expert Guidance
The Canadian insolvency landscape is complex and full of legal nuances. From understanding the intricacies of the Bankruptcy and Insolvency Act and the Companies’ Creditors Arrangement Act to effectively negotiating with diverse creditors (including banks, suppliers, and the Canada Revenue Agency), professional expertise is not just helpful, it is essential.
Why a Licensed Insolvency Trustee (LIT) is Your Best Choice for Business Debt Restructuring:
- Unbiased Advice: LITs are regulated by the Canadian government and are legally required to provide impartial advice on all your options, including both formal restructuring and bankruptcy, ensuring you choose the best path for your unique situation.
- Legal Authority: Only LITs are legally authorized to administer formal restructuring processes like Division 1 Proposals under the BIA. Without an LIT, these powerful tools are unavailable to your business.
- Creditor Negotiation Skills: Our team at Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc. has extensive experience in dealing with all types of creditors. We know their concerns, their processes, and how to negotiate effectively to achieve a consensual agreement.
- Protection from Creditors: An LIT can help you immediately get the “stay of proceedings” you need to stop harassing creditor calls, lawsuits, and collection actions, giving your business crucial breathing room.
- Comprehensive Solutions: We can assess your specific situation, identify the root causes of financial distress, and recommend the most effective path forward, whether informal negotiations or a formal proposal.
7.3 Taking Action: Your First Step Towards a Stronger Future
Don’t let fear, uncertainty, or pride paralyze you. The sooner you seek professional help, the more options you’ll have, and the better the chances of a successful outcome for your business. Every day you delay can limit your choices and increase the risk.
Your first step is simple and without obligation: Contact Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc.
We are experienced Licensed Insolvency Trustees specializing in helping Ontario businesses navigate financial distress and successfully restructure their debts. We offer a free, confidential, no-obligation consultation where we will:
- Listen to your situation without judgment and with genuine empathy.
- Explain all your business debt restructuring options clearly and simply, helping you understand the pros and cons of each.
- Help you understand the best path forward for your company, providing a personalized strategy.
- Provide immediate relief by outlining steps to stop creditor harassment and financial anxiety.
Let us help you lift the burden of debt and guide your business towards a sustainable, successful future. You’ve worked too hard to let debt be the end of your story.
FAQs About Business Debt Restructuring
Q1: What is the main difference between a BIA Division 1 Proposal and CCAA in Canada?
A: A Division 1 Proposal under the restructuring, business debt, avoid bankruptcy, licensed (BIA) is typically used for smaller to medium-sized businesses and has a more defined procedural code and shorter timelines. The Companies’ Creditors Arrangement Act (CCAA) is for larger, more complex corporations, usually with debts over $5 million, and offers more flexibility and longer timelines under court supervision. Both provide a “stay of proceedings” to protect the company from creditor actions.
Q2: Can business debt restructuring help with Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) debt?
A: Yes, certain CRA debts, such as unremitted corporate income tax and GST/HST (excluding employee source deductions, which have super-priority), can be included in a formal BIA Division 1 Proposal. This can help manage or reduce the amount owed to the CRA and effectively stop their collection actions. A Licensed Insolvency Trustee has experience dealing with the CRA and knows how to structure a proposal that addresses these specific debts.
Q3: Will restructuring my business debt affect my personal credit or assets?
A: If your business is incorporated, its debt generally doesn’t directly affect your personal credit unless you have personally guaranteed specific business loans. If you are a sole proprietor or in a partnership, your business and personal finances are legally linked, so business debt will directly impact you personally. A Licensed Insolvency Trustee can help assess the impact on personal guarantees and assets, and advise on strategies to protect your personal finances.
Q4: How long does the business debt restructuring process take?
A: The length varies greatly depending on the chosen path. Informal restructuring can be quick if all creditors agree readily. A BIA Division 1 Proposal has specific timelines but generally takes several months (typically 3-6 months from filing to approval). CCAA proceedings for large corporations can take much longer, sometimes over a year, due to their complexity and the extensive court oversight required.
Q5: What happens if my creditors reject my business debt restructuring proposal?
A: If a BIA Division 1 Proposal is rejected by your creditors or the court, your business is deemed bankrupt. This is a serious consequence. If a CCAA plan is rejected, it does not automatically lead to bankruptcy, giving the company more flexibility to explore other options or negotiate further. This is precisely why expert guidance from a Licensed Insolvency Trustee like Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc. is so important – to craft a proposal that maximizes the chances of acceptance.

Brandon’s Take: The Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc. Difference
As Senior Vice-President of Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc., I’ve seen firsthand the immense pressure business owners face when debt becomes overwhelming. It’s easy to feel isolated and as if there’s no way out. But I want to reassure you: there absolutely is a way forward. Business debt restructuring is not the end of your business; it’s a strategic pivot, a chance for renewal, and often, a catalyst for future success.
What sets us apart at Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc. is our unwavering commitment to not just process, but to people. We don’t just look at numbers and legal statutes; we look at your business, its potential, your vision for its future, and the personal impact on you as an owner. Our approach is empathetic, non-judgmental, and always focused on finding the best solution for your unique situation. We bring not only our deep legal expertise as federally Licensed Insolvency Trustees but also a profound understanding of the practical realities of running a business in Ontario.
We firmly believe in proactive measures. The moment you notice those early warning signs of financial distress, that’s when you should reach out to us. The earlier we engage, the more robust and favourable your options for debt restructuring become. We will stand by you, guiding you through every step, from the initial assessment and planning to negotiating with creditors and rebuilding your business stronger than before. Your success, your peace of mind, and the sustained life of your business are our ultimate goals. Let us be the trusted partner you need to navigate these challenging times.”
Business Debt Restructuring Conclusion: Your First Step Towards a Stronger Future
Business debt doesn’t have to be a dead end. It can be a powerful turning point – an opportunity to restructure, rebuild, and emerge stronger than ever. The journey might seem daunting, and the options complex, but with the right guidance, it’s a path you can navigate successfully.
Don’t wait until it’s too late. The longer you delay, the fewer options become available, and the greater the risk to your business and your personal finances. Taking that first step to seek expert advice is the most powerful and proactive decision you can make right now.
Take Action Today: Contact Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc.
We are Licensed Insolvency Trustees, dedicated to providing clear, actionable, and compassionate advice to businesses across Ontario. We offer:
- Free, Confidential Consultations: Discuss your unique situation without cost, obligation, or judgment.
- Expert Guidance: Understand all your options for business debt restructuring, from informal negotiations to formal proposals under Canadian law.
- A Clear Path Forward: Get a personalized, step-by-step plan tailored specifically to your business’s needs and goals.
- Relief from Pressure: We can help you stop creditor harassment and regain control.
Let us help you lift the burden of debt and guide your business towards a sustainable, successful future. Call us now or visit our website to schedule your free consultation. Your business’s second chance starts here.
Take the first crucial step towards a brighter financial future for your business. Contact Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc. today to schedule your free initial consultation. Your business’s pivot to sustainable success starts now.
Don’t let financial uncertainty dictate your future. If you or your business is struggling with debt, losing sleep, or facing the possibility of legal action, contact Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc. today. We offer a free, confidential consultation to discuss your situation, explain your options in plain language, and help you develop a clear, actionable plan. Our team of Licensed Insolvency Trustees is dedicated to providing the compassionate, professional support you need to regain control and achieve a debt-free life. Take the first step towards a brighter financial future – call us now.
Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc. is licensed by the Office of the Superintendent of Bankruptcy and is a member of the Canadian Association of Insolvency and Restructuring Professionals.
- Phone: 905.738.4167
- Toronto line: 647.799.3312
- Website: https://irasmithinc.com/
- Email: brandon@irasmithinc.com
Disclaimer: This analysis is for educational purposes only and is based on the cited sources and my professional expertise as a licensed insolvency trustee. The information provided does not constitute legal or financial advice for your specific circumstances.
Every situation is unique and involves complex legal and factual considerations. The outcomes discussed in this article may not apply to your particular situation. Situations are fact-specific and depend on the particular circumstances of each case.
Please contact Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc.get in touch with Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc.
About the Author:
Brandon Smith is a Senior Vice-President at Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc. and a licensed insolvency trustee serving clients across Ontario. With extensive experience in complex court-ordered receivership administration and corporate insolvency & restructuring proceedings, Brandon helps businesses, creditors, and professionals navigate challenging financial situations to achieve optimal outcomes.
Brandon stays current with landmark developments in Canadian insolvency law. He brings this cutting-edge knowledge to every client engagement, ensuring his clients benefit from the most current understanding of their rights and options.