As Senior Vice-President at Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc., I’ve seen firsthand the immense pressure and confusion directors face when their company is struggling. Many believe their position offers an impenetrable shield, only to discover too late that their personal assets are very much at risk. My goal here is to cut through that confusion regarding Director liability and D&O insurance, giving you clear, actionable advice to protect yourself. Please keep in mind that we are licensed insolvency trustees, not lawyers. As I caution at the end of my Brandon’s Blog, this article is not meant as legal advice and does not replace or eliminate the need for you to get the advice of your lawyer.
D&O Insurance Key Takeaways
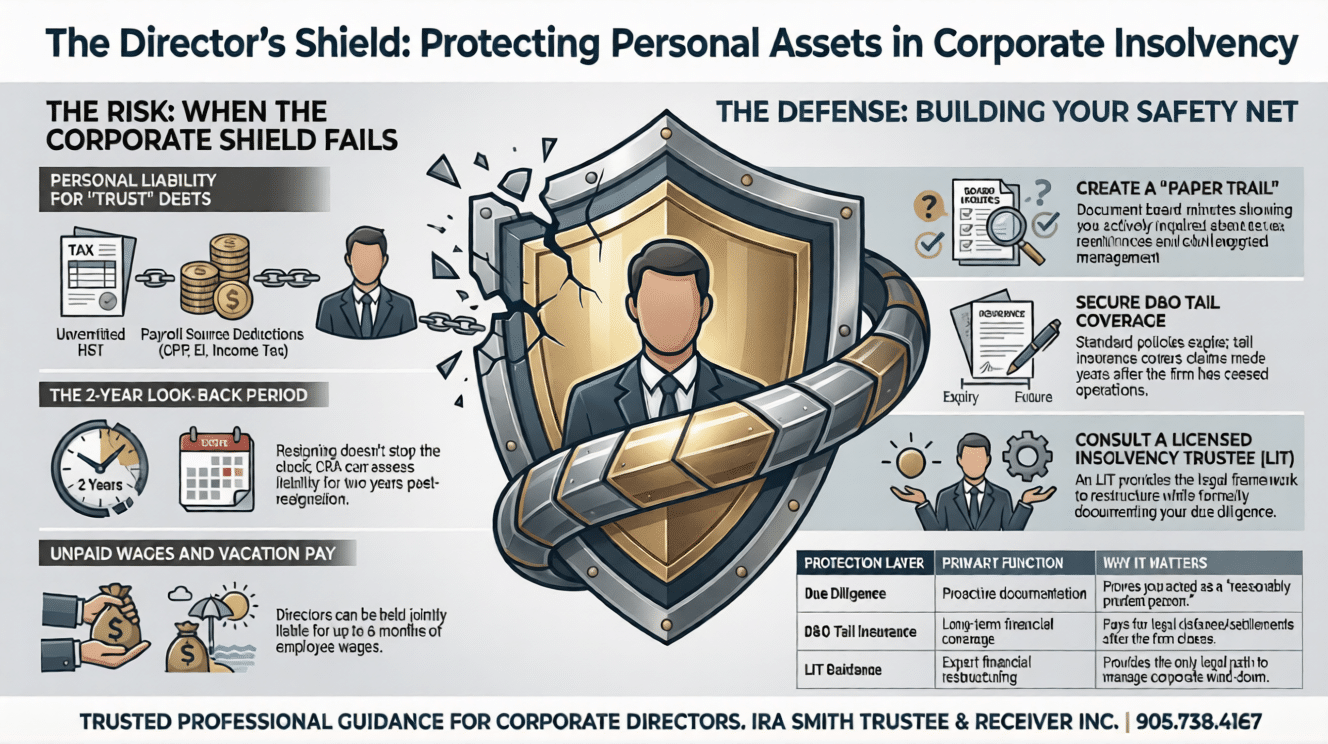
- Personal Liability is Real: Directors can be held personally responsible for certain company debts, such as HST, payroll source deductions (CPP, EI, income tax), and employee wages, in Canada.
- “Due Diligence” is Your Defence: Your best protection is to show you acted with the care a reasonable person would to prevent the debt. This must be proactive, well-documented, and create a solid “paper trail.”
- Timing Matters: Resigning from a board after debts have piled up does not automatically free you. The Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) can look back two years from your resignation date to assess liability.
- D&O and Tail Insurance are Crucial: Directors & Officers liability insurance (D&O insurance), especially “tail” or “run-off” coverage, is a vital safety net for protecting your personal assets from claims that arise later, long after the company has ceased operations.
- Seek Expert Advice Early: Consulting with a Licensed Insolvency Trustee (LIT) like Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc. as soon as financial trouble appears can provide crucial guidance and help build your defence, ensuring you act correctly at critical junctures.
D&O Insurance Introduction: Navigating the Perilous Waters of Corporate Distress
Many directors sleep soundly, believing their company’s legal structure shields them completely. But when a business faces a wind-down, that shield can crack, exposing personal assets to serious risks. Imagine losing your home or your life savings because of corporate debt you thought was not yours. This is a very real possibility for directors in Canada. Ignorance is not bliss; it’s personal liability.
As a director, you take on significant responsibility. When a company thrives, you share in its success. But when it struggles, especially towards a wind-down, your personal finances can be targeted. Laws exist to ensure that certain debts are to be paid by the directors, even if the corporation cannot. These include unpaid sales tax (HST), unremitted payroll deductions (like income tax, Canada Pension Plan, and Employment Insurance). These are called statutory obligations or “trust amounts” because the company holds them on behalf of the government(further described below). Unpaid employee wages and vacation pay are also a director’s liability.
Timing is everything. Waiting until a crisis hits is often too late. Early consultation with a Licensed Insolvency Trustee can provide the critical guidance and “due diligence” paper trail you need. This guide will walk you through these risks, show you how to build your defences, explain formal wind-down procedures, and highlight the crucial role of D&O insurance, especially D&O tail coverage. The “due diligence” shield is your only hope.
1. D&O Insurance: The Director’s Evolving Role in Financial Difficulty
Being a director carries important duties. These duties become even more complicated when a company runs into financial trouble. An insolvent company transforms the expectations and legal requirements placed upon you.
1.1 Why Director Protection is Paramount During a Wind-Down
Director protection is paramount during a wind-down because the usual “corporate veil” that shields directors from personal liability can be pierced under specific circumstances. Normally, directors work to make the company successful and grow its value for shareholders. However, if the company becomes insolvent (cannot pay its bills), your main duty shifts. You must now focus on protecting the company’s assets for its creditors, not just its shareholders.
The idea that a company is a separate legal entity from its owners and directors usually protects directors from personal responsibility for the company’s debts. But under specific Canadian laws, this protection can be “pierced,” meaning your personal assets – your home, savings, and investments – can be at risk. This is why understanding these risks and proactively protecting yourself is so important. As a Senior Vice-President at Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc., I have seen the devastating personal impact when directors are unaware of these shifts in liability.
1.2 Defining a Corporate Wind-Down: More Than Just Closure
Defining a corporate wind-down means understanding it is a formal, structured process of ending a business, not simply locking the doors. It involves settling debts, selling assets, and dealing with all legal duties. A wind-down can happen voluntarily, or through formal insolvency proceedings like bankruptcy or an arrangement with creditors.
The moment a company becomes insolvent – meaning it can no longer pay its bills as they become due – is a very important point. This is a critical turning point where your duties as a director change, and the risk of personal liability for certain debts increases significantly. This guide focuses on helping you navigate this complex process, emphasizing that early action and expert advice from professionals like Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc. are your best allies.
1.3 The Shifting Sands of Fiduciary Duties: From Shareholders to Creditors
The shifting sands of fiduciary duties mean that your primary legal obligations as a director change from serving shareholders to prioritizing the benefit of creditors once a company faces insolvency. As a director, you have “fiduciary duties.” This means you must act honestly and in good faith, always doing what’s best for the corporation. When a company is doing well, this usually means working to increase profits and shareholder value.
However, once a company is insolvent or close to it, your duty shifts. You must then prioritize the interests of the company’s creditors (those it owes money to). This means making sure company assets are used to pay debts, not to benefit shareholders or yourself. Ignoring this shift can lead to personal liability, especially if you continue to make payments to shareholders or certain creditors while leaving others (like the CRA or employees) unpaid. Understanding this change is fundamental to director protection during a wind-down.
2. D&O Insurance: Key Areas of Personal Liability Risk for Directors
As a director in Canada, certain debts can fall onto your shoulders if the company can’t pay them. These are often called “trust amounts” or statutory obligations, and they are a primary focus for government agencies, representing significant personal liability risks.
2.1 CRA Director Liability: HST and Source Deductions
Directors can be personally liable for specific tax debts owed to the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) if the company fails to remit them.
What personal liabilities do directors face in Canada for a company’s unpaid taxes (HST, source deductions) and wages during a wind-down?
In Canada, directors can be held personally responsible for:
- Unremitted Payroll Deductions: These are amounts taken from employee paycheques for income tax, Canada Pension Plan (CPP) contributions, and Employment Insurance (EI) premiums. The company collects these amounts but holds them “in trust” for the government.
- Unremitted GST/HST: This is the Goods and Services Tax / Harmonized Sales Tax collected from customers by the business. Like payroll deductions, these are “trust amounts” that the company holds on behalf of the CRA.
When a company uses these funds to keep the business going instead of sending them to the CRA, directors can become personally liable. The Income Tax Act and the Excise Tax Act (for GST/HST) outline these liabilities.
The CRA doesn’t automatically go after directors. It goes through certain steps to assess personal liability:
- Failed Collection from the Corporation: The CRA must first try and fail to collect the unpaid amounts directly from the company. This usually involves issuing assessments and taking collection actions.
- Assessment Within Two Years of Resignation: The CRA must send an assessment notice to the director within two years from the date they last stopped being a director. This means resigning doesn’t instantly remove your risk; the clock starts ticking then. Timing is everything. Resigning from a board after the debt has accrued does not stop the CRA.
- Lack of Due Diligence: If the director cannot prove that they “exercised the degree of care, diligence, and skill to prevent the failure that a reasonably prudent person would have exercised in comparable circumstances”, then they are personally liable. This “due diligence” defence is your most crucial protection, which we will discuss in detail.
Directors can also face penalties and interest on these unremitted amounts.
2.2 Unpaid Wages and Director Responsibility
Directors can also be personally liable for unpaid employee wages. This liability is governed by provincial laws, such as the Ontario Employment Standards Act (ESA) and the Ontario Business Corporations Act (OBCA).
The scope of this liability typically covers:
- Up to 6 months of unpaid wages: This includes regular pay, commissions, and potentially some bonuses owed to employees.
- Up to 12 months of vacation pay: This covers vacation pay that has accrued and is due to employees.
Directors are “jointly and severally liable” for these amounts, meaning an employee can pursue one or all directors for the full amount owed. This means that if there are multiple directors, an employee could sue just one director for the entire amount, leaving that director to seek contributions from the others.
Certain conditions must be met for directors to be held liable for wages, such as the corporation being unable to pay, going bankrupt, or being formally wound up. It’s also important to note that claims for unpaid wages usually must be brought within a specific timeframe, often 6 months from when the wages were due or from the start of bankruptcy/liquidation proceedings.
2.3 Other Potential Liabilities
Beyond taxes and wages, directors can face other personal liabilities depending on the specific circumstances and actions taken:
- Personal Guarantees: If you personally guaranteed a company loan, lease, or line of credit, you are directly responsible for that debt if the company defaults. These guarantees are separate from statutory liabilities and are a direct contractual obligation.
- Environmental Liabilities: In Ontario, under the Environmental Protection Act, directors can be personally liable for the cost of cleaning up contaminated land that the corporation owned or operated, even after the company has dissolved. This is a severe and often overlooked liability.
- Fraudulent or Oppressive Conduct: Directors can be held liable if they engage in fraud, mismanage the company’s assets for personal gain, or act in a way that unfairly harms creditors or shareholders. Examples include knowingly transferring assets to avoid creditors or making decisions that are clearly not in the company’s best interest but benefit the director.

D&O insurance
3. The Proactive Director: Building Defences Before the Storm Hits
The best defence against personal liability is to be proactive. This means taking steps before financial problems become too severe, establishing practices that demonstrate responsible oversight and diligence.
3.1 Establishing Robust Corporate Governance and Internal Controls
Establishing robust corporate governance and internal controls is foundational for directors to demonstrate they are fulfilling their duties and to build a strong “due diligence” defence. Good governance means having clear rules and practices for how the company is run. This includes:
- Financial Oversight: Make sure there are proper systems for tracking all money coming in and going out. This includes accurate accounting records and regular financial reporting to the board.
- Statutory Remittance Systems: Implement clear, non-negotiable procedures to ensure HST and payroll deductions are collected and sent to the CRA on time. Don’t just assume it’s happening; verify it regularly.
- Detailed Records: Keep accurate and complete records of all financial transactions, tax filings, and board meetings. This creates your crucial “paper trail.”
- Regular Board Meetings: Attend all meetings and make sure that financial reports are reviewed and discussed thoroughly. Board minutes should reflect these discussions.
- Segregation of Duties: Ensure that no single person has control over all financial processes (e.g., the person who writes cheques should not be the same person who reconciles bank statements). This reduces the risk of fraud or oversight.
3.2 Implementing Effective Financial Risk Assessment and Management
Implementing effective financial risk assessment and management practices allows directors to identify, monitor, and mitigate potential financial pitfalls before they escalate into personal liability risks. It’s crucial to identify financial problems early.
- Watch for Warning Signs: Keep a close eye on key financial indicators such as consistent negative cash flow, late bill payments, declining sales, increasing debt, or unusual changes in expenses. These are clear signs that the company might be in trouble.
- Regular Financial Reviews: Don’t just glance at financial reports. Understand them. Ask challenging questions about the company’s ability to meet its current and future obligations, especially those related to statutory remittances and employee wages.
- Cash Flow Projections: Insist on realistic cash flow projections and review them regularly. This helps predict potential shortfalls in time to address them.
- Seek Early Advice: If you see problems, get professional financial advice before things get out of control. This can involve bringing in outside accountants or, ideally, a Licensed Insolvency Trustee like Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc., to conduct a financial review or advise on options.
3.3 Maintaining Meticulous Records and Due Diligence Documentation (The “Paper Trail”)
Maintaining meticulous records and due diligence documentation is not just good practice; it is the cornerstone of your personal defence against liability, creating the “paper trail” that proves you acted responsibly.
How can a director use the “due diligence” defence to avoid personal liability for corporate tax debts and unpaid wages in Canada?
The “due diligence” defence is your most powerful tool to avoid personal liability for CRA debts and unpaid wages. This defence argues that you are not liable if you “exercised the degree of care, diligence, and skill to prevent the failure that a reasonably prudent person would have exercised in comparable circumstances.” This means you must show you took reasonable steps to prevent the company from failing to pay its statutory obligations or employee wages.
Here’s what that means and how to build your “paper trail”:
- Proactive, Not Reactive: Due diligence is about preventing problems, not trying to fix them after they’ve happened. Actions taken after a debt has accrued are often too late to establish this defence. You need to show foresight and preventive action.
- Inquire and Challenge: Regularly ask management about the company’s financial health, specifically regarding statutory remittances (HST, CPP, EI, income tax) and wage payments. Don’t just accept verbal assurances; demand proof.
- Request and Review Documents: Ask for and carefully examine financial statements, tax filings, payroll records, and proof of remittance. Make sure these documents clearly show that all obligations are being met on time.
- Document Everything: Keep detailed minutes of board meetings where financial matters were discussed. Record your specific questions, management’s answers, any concerns you raised, and any actions agreed upon to address those concerns. If you dissent from a decision you believe is risky, ensure your dissent is formally recorded.
- Seek Expert Advice: If you have concerns, recommend bringing in outside financial or legal experts. Document this recommendation and their advice. Relying on professional advice from a Licensed Insolvency Trustee (LIT) like Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc. can be a critical part of your due diligence, showing you sought expert guidance.
- Challenge Mismanagement: If you believe the company is mismanaging funds, particularly “trust amounts,” you must voice your concerns forcefully and take steps to prevent the failure. Simply asking questions might not be enough if you don’t follow up and escalate your concerns or take corrective action. This could include insisting on a formal insolvency process if appropriate.
Keep in mind that “inside directors” (those actively involved in day-to-day operations) are held to a higher standard than “outside directors” (those less involved), as they have greater access to information and influence over company operations.
This “paper trail” is your best legal defence. It proves you took reasonable steps to prevent the default, even if the default ultimately occurred. Without this documentation, it becomes your word against the CRA’s or an employee’s, which is a very difficult position to be in.
Aspect of Due Diligence | Description | Why it’s Important |
|---|---|---|
Regular Board Meetings | Attending and actively participating in all board meetings. | Demonstrates engagement and opportunity to oversee. |
Financial Review | Consistently reviewing financial statements, cash flow, and projections. | Identifies financial distress early; ensures awareness of the company’s ability to pay debts. |
Inquiry & Verification | Asking specific questions about tax remittances and wage payments. Requesting proof of payment. | Proves you didn’t just assume; you actively sought assurance. |
Documenting Concerns | Recording any concerns raised and management’s responses in board minutes. | Creates the “paper trail” needed to show proactive effort. |
Seeking Expert Advice | Recommending and acting on advice from financial or legal professionals (e.g., LIT). | Shows you sought specialized expertise to fulfill your duties. |
Taking Corrective Action | Insisting on changes, payment plans, or formal insolvency if necessary. | Demonstrates you took tangible steps to address issues. |
3.4 Understanding and Managing Key Stakeholder Relationships
Understanding and managing key stakeholder relationships during a wind-down means strategically engaging with creditors, employees, and government agencies to potentially mitigate future claims and foster cooperation. Maintaining good relationships with the CRA, employees, and other creditors is important. Open and honest communication, when appropriate and with legal advice, can sometimes help navigate difficult situations, such as negotiating payment plans or explaining the company’s financial state transparently. This proactive engagement can sometimes prevent or reduce aggressive collection actions against directors personally.
4. D&O Insurance And The Strategic Decision-Making During a Wind-Down: Actionable Steps for Protection
When dealing with an insolvent corporation, every decision counts. Taking the right steps at the right time is crucial for director protection, especially as the situation moves towards a formal wind-down.
4.1 Immediate Actions Upon Recognizing Irremediable Distress
Distressed companies must take Immediate action upon recognizing financial distress. Prioritizing legal obligations and seeking expert advice to minimize personal liability is key. If it becomes clear the company cannot recover, you must act quickly and decisively:
- Prioritize Statutory Remittances: Immediately ensure that all HST owing and payroll deductions are paid. Do not use these “trust funds” to keep the business alive, as this is a direct path to personal liability. These payments take precedence over almost all other unsecured debts.
- Evaluate Future Payments: Stop making payments to general creditors if it jeopardizes the payment of statutory debts, or if doing so could be seen as an unfair preference to one creditor over others, which can have legal consequences.
- Consider Resignation (Carefully): While resigning might seem like a solution, it’s not a magic bullet. For CRA debts, the two-year look-back period starts from your resignation date. This means you can still be held liable for debts incurred while you were a director, even after you leave the board. Resignation should be properly documented and registered with corporate registries. Furthermore, resigning without ensuring proper governance and advice can sometimes be seen as an avoidance tactic, further complicating matters.
4.2 Engaging the Right Professional Advisors: Your Shield and Guide
Engaging the right professional advisors is perhaps the most critical step you can take when a company faces irremediable distress, as they provide essential expertise and legal protection.
- The Indispensable Role of a Licensed Insolvency Trustee (LIT): An LIT, like Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc., is the only professional legally able to administer formal financial restructuring insolvency proceedings in Canada. We are experts in Canadian insolvency law, with vast experience in guiding companies and directors through complex financial distress. We can help you:
- Assess the company’s true financial situation, giving you an unbiased and accurate picture.
- Advise on all available options, including restructuring (like a Division I Proposal under the BIA or a Plan of Arrangement under the Companies’ Creditors Arrangement Act) or formal corporate bankruptcy.
- Explain the specific director liabilities you face, providing clarity on your personal exposure.
- Help document your “due diligence” actions, which are vital for your defence, ensuring you have the necessary “paper trail.”
- Guide the company through formal wind-down procedures in a structured way that minimizes director risk, ensuring compliance with all legal requirements.
- Communicate effectively with creditors, including the CRA, on your behalf, often easing tension and facilitating resolutions.
- Legal Counsel: You should also consult a lawyer who specializes in corporate or insolvency law to understand your specific legal position, potential defences, and any broader corporate law implications.
4.3 Balancing Competing Interests: Navigating Stakeholder Demands
Balancing competing interests means navigating the diverse and often conflicting demands of various stakeholders (employees, suppliers, banks, the CRA) while ensuring legal compliance and minimizing director liability. During distress, many groups will demand payment. An LIT can help you understand your legal duties to each group and navigate these competing demands fairly and legally, especially regarding preferential payments.
4.4 Managing Communications Effectively and Transparently
Managing communications effectively and transparently involves carefully planning what, when, and how to communicate with stakeholders to maintain trust and avoid exacerbating legal or reputational issues. Communicating with stakeholders during a wind-down is sensitive. Get advice on what, when, and how to communicate to avoid further liability or distress, as missteps can be costly.
4.5 Boardroom Protocols and Decision-Making under Pressure
Boardroom protocols and decision-making under pressure require strict adherence to governance principles and meticulous documentation, especially when the company’s solvency is at stake. Ensure all significant decisions are properly documented in board minutes, especially those related to financial distress, expert consultations, and steps taken to address liabilities. This reinforces your due diligence.

5. Navigating Formal Wind-Down Procedures: A Director’s Overview
Navigating formal wind-down procedures means understanding the specific legal frameworks available in Canada for closing a business, each with distinct implications for directors. When a company cannot simply close its doors, formal legal procedures come into play. These procedures have specific rules for directors and are administered by a Licensed Insolvency Trustee.
5.1 Voluntary Corporate Dissolution: A Controlled Exit
Voluntary corporate dissolution through an orderly liquidation is a controlled exit strategy. It makes sense for companies with few or no debts, or where all debts can be paid off in full. It’s a structured way to close the business, often involving articles of dissolution filed with the government. In Ontario, if the company owns land, Crown (government) consent might be needed for dissolution. If there are significant debts that cannot be paid, a voluntary dissolution is not possible without creditor agreement.
5.2 The Bankruptcy and Insolvency Act (BIA): Director Implications
The Bankruptcy and Insolvency Act (BIA) is the primary federal law governing corporate bankruptcy and financial restructuring proposals in Canada, outlining the rules and regulations for a company unable to meet its financial obligations.
When a company files for bankruptcy under the BIA, a Licensed Insolvency Trustee is appointed. The trustee takes control of the company’s assets to sell them and pay creditors. This process often triggers director liabilities for unpaid wages and statutory remittances, as the company’s inability to pay usually becomes definitively clear. Our role as LITs is to manage this process fairly and transparently, and we can advise directors on their specific obligations and potential liabilities during this time, helping them understand how the bankruptcy process impacts their personal situation.
5.3 Companies’ Creditors Arrangement Act (CCAA): Restructuring vs. Liquidation
The Companies’ Creditors Arrangement Act (CCAA) is a federal law typically used by larger companies with debts over $5 million to restructure their finances, offering protection from creditors during the process. It allows a company to restructure its finances while being protected from its creditors. Directors play a significant role in developing and implementing the restructuring plan, often remaining in control under court supervision. If restructuring fails, the company may move to liquidation, often under the BIA. Directors still face the same personal liabilities under the CCAA as they would under the BIA, and their conduct during the restructuring process is subject to scrutiny.
5.4 The Winding-up and Restructuring Act : Specific Scenarios
The Winding-up and Restructuring Act is another federal statute that applies mainly to federally incorporated companies, or those in specific regulated industries like banks or insurance companies. It provides a framework for both winding-up (liquidation) and restructuring, similar to the BIA and CCAA, but tailored for these specific entities. Directors of companies subject to proceedings under this Act face similar personal liability risks as under the BIA, making due diligence and expert advice just as crucial.
6. The Essential Safety Net: D&O Insurance and Tail Insurance
Even with the best due diligence, directors can still face claims. This is where D&O insurance becomes a critical safety net for your personal assets, providing protection when legal challenges arise.
6.1 Understanding D&O Insurance
Understanding D&O insurance means recognizing it as a policy designed to protect company leaders from personal financial loss due to lawsuits stemming from their corporate decisions. D&O insurance protects company leaders – directors and officers – from personal financial loss if they are sued for decisions or actions made in their roles. It typically covers:
- Legal Defence Costs: Lawyers’ fees and other costs to defend against a lawsuit, which can be astronomical even if the claim is baseless.
- Settlements and Awards: Money paid to resolve a claim or awarded by a court, up to the policy limits.
It’s a common belief that only large corporations need D&O insurance. This is a misconception. Small and private businesses are just as vulnerable to claims, and without the deep pockets of larger firms, these claims can be financially devastating for individual directors. Even a director for a non-profit organization can face D&O claims.
However, D&O insurance does not cover everything. It generally excludes:
- Deliberately fraudulent or criminal acts.
- Intentional non-compliance with laws.
- Fines and penalties (which can be a significant part of CRA assessments, as these are typically considered punitive rather than compensatory).
- Bodily injury or property damage claims (these are covered by other types of insurance, such as general liability).
- Claims based on personal guarantees.
The policy often has different “Sides” of coverage: “Side A” directly protects individual directors when the company cannot indemnify them (e.g., due to insolvency or legal prohibition), which is especially important during a wind-down when the company’s assets may be gone. “Side B” reimburses the company for indemnifying its directors, and “Side C” covers the company itself for certain claims.
6.2 The Critical Need for Run-Off (Tail) Coverage
The critical need for run-off (tail) coverage arises because most D&O policies are “claims-made,” meaning they only cover claims made and reported while the policy is active, leaving directors exposed after a company ceases operations.
What is D&O “tail coverage” and why is it essential for directors during a corporate wind-down or insolvency?
Most D&O policies are “claims-made.” This means they only cover claims that are made and reported while the policy is active. If your company closes and the policy expires, any claim made after that date, even if it relates to actions taken before the closure, will generally not be covered. This is a huge gap in protection, especially given that lawsuits can take years to materialize.
This is where “tail coverage” (also known as “extended reporting period,” “ERP,” or “run-off” coverage) becomes essential. Tail coverage extends the time you have to report claims under your D&O insurance policy.
- Purpose: It protects directors from claims that surface months or even years after the company has ceased operations or the D&O policy has expired, but which relate to events that occurred while the original policy was active.
- Why it’s Vital: Claims often emerge long after a company closes its doors. Creditors, former employees, or even the CRA can bring actions years later (e.g., the CRA’s two-year look-back for director assessments). Without tail coverage, your personal assets could be exposed to defence costs and settlements, with no corporate entity left to help you. The company itself, having wound down, would not be there to indemnify you.
- Coverage Period: Tail coverage typically lasts for a specified period, often six years, to align with various statutes of limitation for different types of claims. This ensures a long-term safety net.
Think of your regular D&O policy as a security camera that only records while plugged in. Tail insurance lets you review the footage (report claims) even after the camera is unplugged (policy expires), providing an essential historical record of coverage.
6.3 Maximizing Your Policy’s Effectiveness: Beyond Just Having D&O Insurance Coverage
Maximizing your D&O insurance policy’s effectiveness goes beyond simply purchasing D&O insurance; it requires a deep understanding of its terms and proactive management of its features.
- Review Your Policy Thoroughly: Understand its limits, exclusions, and how it behaves during insolvency or a change of control (e.g., a sale of the company). Don’t just file it away; read the fine print.
- Consider Increased Limits: When a company is winding down, its own assets may be gone, placing more reliance on D&O insurance coverage. Therefore, consider whether your existing limits are adequate given the potential liabilities.
- Negotiate Tail Coverage Early: Ideally, tail coverage should be discussed and secured as part of the D&O insurance renewal process or when the company first anticipates a wind-down, not as an afterthought. This ensures continuous protection.
- Understand Claim Reporting Requirements: Be aware of the deadlines and procedures for reporting potential claims to your insurer. Late reporting can lead to denied coverage.
6.4 Regularly Reviewing and Updating D&O Insurance Policies
Regularly reviewing and updating all insurance policies is crucial because your D&O insurance and tail coverage needs can change over time, necessitating adjustments to maintain adequate protection. As your company evolves, or as the risk landscape changes, so should your insurance coverage. Review your policies regularly with an insurance professional to ensure you have adequate protection for current and potential future liabilities.

7. The Post-Wind-Down Landscape: Lingering Concerns for Directors
Even after a company has formally wound down, a director’s duties and potential liabilities don’t always vanish immediately, often leaving lingering concerns that require continued vigilance.
7.1 Ongoing Scrutiny and Potential Investigations
Ongoing scrutiny and potential investigations mean that regulatory bodies or former stakeholders can initiate legal actions or probes years after the company is gone. Regulatory bodies, like the CRA, or former employees, or even court-appointed trustees, can initiate investigations or lawsuits years after the company is gone. Your meticulous due diligence records and D&O insurance tail coverage are your primary defences here, providing documented proof and financial protection.
7.2 Record Retention Requirements and Obligations
Record retention requirements and obligations mean directors have a continuing legal duty to ensure company records are properly kept and accessible, even long after dissolution. This is critical for defending against post-wind-down claims and supports your due diligence defence, proving your past actions.
7.3 Reputational Management and Future Opportunities
Reputational management and future opportunities are important considerations for directors, as how a wind-down is handled can significantly impact their professional standing. While not a direct legal liability, managing your professional reputation during and after a wind-down is important for future career opportunities. Transparency and demonstrating responsible conduct, supported by your documented due diligence and adherence to legal processes, can help protect your professional standing.
8. Frequently Asked Questions: Director Liability & D&O Insurance
Q. Does standard D&O insurance protect me after my company closes?
A: Standard D&O insurance typically only covers claims made while the policy is active. To protect yourself from claims that arise after a business has ceased operations, you must secure “tail coverage” (also known as “run-off” coverage), which extends the reporting period for several years.
Q: Can the CRA hold me personally liable even if I resigned?
A: Yes. In Canada, the CRA has a two-year look-back period from the date of your resignation to assess personal liability for unremitted HST and payroll deductions. Resigning does not instantly erase your risk for debts that accrued while you were a director.
Q: What specific debts am I personally responsible for as a director?
A: Under Canadian law, directors can be held personally liable for “trust amounts,” which include:
- Unremitted GST/HST collected from customers.
- Payroll Source Deductions, such as employee income tax, CPP, and EI.
- Employee Wages and Vacation Pay typically cover up to six months of wages and twelve months of vacation pay.
Q: How does the “due diligence” defence work in Canada?
A: The due diligence defence allows a director to avoid personal liability if they can prove they exercised the degree of care, diligence, and skill that a “reasonably prudent person” would have to prevent the failure to pay. This requires a proactive, well-documented “paper trail” showing you questioned management and demanded proof of payments.
Q: Why is a Licensed Insolvency Trustee (LIT) necessary during a wind-down?
An LIT is the only professional in Canada legally authorized to administer formal insolvency proceedings. Consulting an LIT early, such as Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc., helps you assess the company’s financial state, understand your specific exposure, and document your due diligence to protect your personal assets.

D&O Insurance Conclusion: Proactive Protection as the Ultimate Defence
The role of a director in a company facing financial distress is challenging and carries significant personal risk. The idea that the corporate veil will always protect your personal assets is a dangerous myth. As we’ve discussed, specific laws in Canada hold directors personally liable for unremitted HST, payroll source deductions, and unpaid employee wages. These liabilities are not theoretical; they are enforced daily.
Recap of Key Director Protection Strategies
To summarize, your best defences are:
- Understand Your Liabilities: Know precisely where your personal assets are at risk under Canadian and Ontario law.
- Practice Proactive Due Diligence: Always act with care, diligence, and skill. Document every step you take to prevent corporate default, creating a robust “paper trail” that can withstand scrutiny.
- Act Early: Timing is critical. Your actions and decisions before a crisis hits are far more effective than reactive measures. Resignation, without prior due diligence, offers limited protection, as the CRA’s look-back period can still catch you.
- Secure Proper Insurance: Ensure you have comprehensive D&O insurance, and critically, D&O insurance tail coverage, to protect you from claims arising after the company winds down and its original D&O policy expires.
The Unwavering Importance of Professional Guidance
Navigating the complexities of director liability and corporate wind-downs is not something you should do alone. The laws are intricate, the financial stakes are high, and the potential impact on your personal financial well-being is immense. Trying to manage these issues without expert guidance can lead to costly mistakes and missed opportunities for protection.
Empowering Directors Through Knowledge and Diligence
Taking on a directorship is a serious commitment, one that comes with both privileges and responsibilities. With the right knowledge and a diligent approach, you can significantly reduce your personal risk, even when your company faces its most challenging times. Being informed and acting proactively are your strongest shields.
Don’t wait until it’s too late. If your company is facing financial difficulty, or if you have concerns about your personal liability as a director, the time to act is now.
Brandon’s Take: Don’t Let ‘Hope’ Be Your Strategy
As a Senior Vice-President at Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc., I’ve unfortunately seen too many directors come to us when it’s almost too late. They hoped things would turn around. They hoped they were protected. Hope is not a strategy when your personal assets are on the line.
The laws are clear: if you are a director, and your company owes money for HST, source deductions, or wages, the government and employees can come after you personally. This isn’t theoretical; it happens every day. Even with D&O insurance, there are exclusions and limitations.
What truly protects you is a clear, documented history of responsible action – your “due diligence.” It means asking the tough questions, demanding clear answers, and showing that you actively tried to prevent the problems, not just reacted to them. This paper trail, combined with the right D&O insurance, especially that critical tail coverage, is your shield.
Contact Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc. Today
Don’t let uncertainty put your personal finances at risk. If your company is facing financial challenges or if you’re concerned about your personal liability as a director, take the proactive step.
Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc. has the expertise and experience to guide you through these perilous waters. As Licensed Insolvency Trustees, we are uniquely qualified to assess your company’s financial situation, advise on the best course of action, and help you understand and mitigate your personal risks. We can help you understand your options, assess your personal risk, and develop a strategy to protect your future. Our approach is empathetic, non-judgmental, and focused on finding the best possible outcome for you and your company.
Contact us for a free, confidential consultation. The sooner you act, the more options you have, and the better protected you will be. Let us help you navigate your path to a brighter financial future.
Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc. is licensed by the Office of the Superintendent of Bankruptcy and is a member of the Canadian Association of Insolvency and Restructuring Professionals.
- Phone: 905.738.4167
- Toronto line: 647.799.3312
- Website: https://irasmithinc.com/
- Email: brandon@irasmithinc.com
Disclaimer: This analysis is for educational purposes only and is based on the cited sources and my professional expertise as a licensed insolvency trustee. The information provided does not constitute legal or financial advice for your specific circumstances.
Every situation is unique and involves complex legal and factual considerations. The outcomes discussed in this article may not apply to your particular situation. Situations are fact-specific and depend on the particular circumstances of each case.
Please contact Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc.get in touch with Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc.
About the Author:
Brandon Smith is a Senior Vice-President at Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc. and a licensed insolvency trustee serving clients across Ontario. With extensive experience in complex court-ordered receivership administration and corporate insolvency & restructuring proceedings, Brandon helps businesses, creditors, and professionals navigate challenging financial situations to achieve optimal outcomes.
Brandon stays current with landmark developments in Canadian insolvency law. He brings this cutting-edge knowledge to every client engagement, ensuring his clients benefit from the most current understanding of their rights and options.













