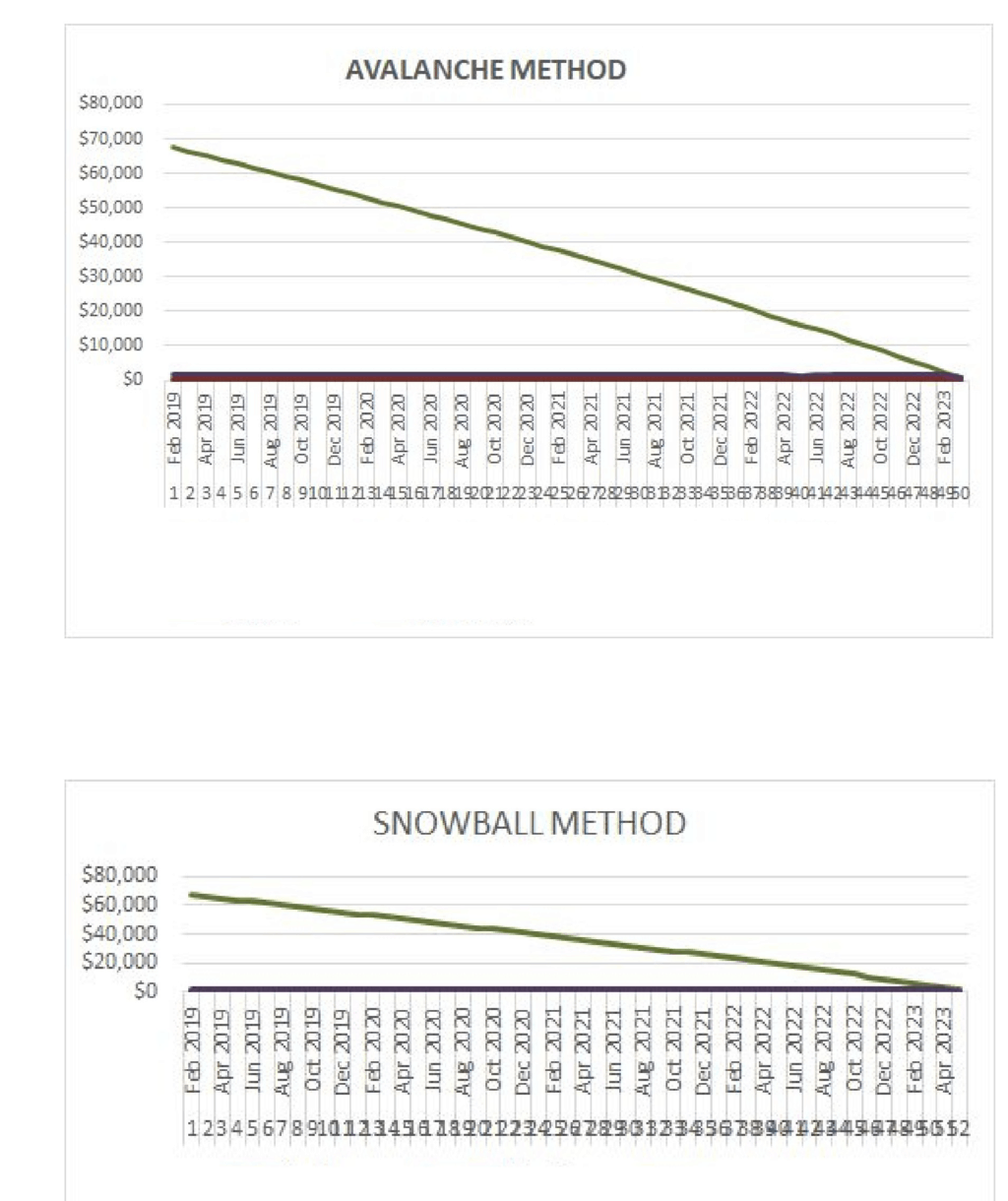
If you would rather listen to the audio version of this money saving apps Canada Brandon’s Blog, please scroll to the bottom and click on the podcast.
Money saving apps Canada: Introduction
If you have followed Brandon’s Blog for any time, you will know that I have written many articles on:
You will also know that I am a big cheerleader for always having an emergency savings fund in the event of, well, an unforeseen emergency. Technology has now met the world of finance. There are apps for both the iPhone and Android that you can use to automatically put money away to build up an emergency fund. These apps that help you save money Canada also help you invest the money. The purpose of this blog is to introduce you to some of these money saving apps Canada that help you save money in Canada.
All of the four money saving apps Canada I mention here are Canadian applications. These apps are for both iPhone and Android. They are apps to help you save money. All links to these fintech apps indicated below are for information only used for this review. They are not affiliate links and I do not earn any money if you end up registering for any of them.
Money saving apps Canada: KOHO
This is one of several Canadian fintech applications. This is how Koho works. When you join and download and install the application, you’ll enter your details. Koho will send you a card powered by Visa. The easiest way to think of it is that Koho works like a prepaid Visa Card. What you want to do is put funds on it as soon as you get your Koho Visa card. You can do this by e-transfer. E-transfers are normally accepted the same-day. You can also set up regular transfers from your pay.
As an example, let’s say you place directly from your regular pay a total of $1,000 a month on your Koho card for your regular spending. Set it up for your groceries, restaurants, coffee purchases as an example. Anything that you would either use cash, a debit card or credit card for. So things like your monthly rent or mortgage payment would not be paid for from your Koho card.
Once your funds are on your Koho card, you trigger it by going to buy your normal purchases with it. The first time you use the Koho card for a purchase you simply enter your PIN to activate it.
Koho is truly great about being a no-fee financial solution. There are no account charges, there are no transfer costs. If you spend a service charge for loading your Koho card with an e-transfer, they refund it back to you. That is why I include it in this list of money savings apps Canada.
Money saving apps Canada: Koho turn your savings on
Koho is my favourite of all the apps to save cash. When your card is turned on, you want this to be your only way of spending. This is because it is actually going to keep you in line. Koho tracks your spending for you. Wherever you spend your cash making use of the Koho card, it will instantly be tracked and classified in the app. Koho will also send you an alert saying, “you’ve spent this much in this place.” Koho provides all the information to you digitally, so it can avoid the need to keep spreadsheets or notes of your spending.
What is unique about Koho is it, in fact, alters your spending behaviour. It will:
- record all your transactions, once it obtains some information;
- will actually tell you your average costs by the week or the month; and
- make predictions of how much you’re possibly going to spend based upon your present spending behaviour.
When you see those numbers, you start to reconsider the purchases you make.
The other manner in which it alters your behaviour is since you can only spend the cash that you’ve packed onto your Koho card, you look for deals and ways to save a lot more carefully than you would on a credit card or even your debit card.
When you open up the Koho application, your spendable amount is right at the top which is all the cash that you have to spend, so you’re very cautious with how you use it. You may not think this would be a method to substantially change your spending actions, but it really is.
Koho is an app that can really stop you from buying stupid things. Now you are saving. Now you have to be religious about transferring those savings every month to an investment account so that you start building up your emergency savings fund.
Money saving apps Canada: Royal Bank of Canada NOMI
The next of my money saving apps Canada is from Royal Bank. You have already probably seen commercials on television for the Royal Bank of Canada (RBC) fintech app NOMI (named for “know me”). The commercial shows two friends talking. One tells the other about his bank’s app that squirrels away cash to his savings account automatically and wonders why RBC is not called the “Squirrely Bank”.
RBC NOMI app is another one of the Canadian apps that help you save cash. It advertises itself as a simple way to manage your day-to-day spending. It makes handling your day-to-day spending as basic as can be. While you’re out living your hectic life, NOMI keeps an eye on your cash and ensures you’re on the right financial track.
NOMI assists you handle your day-to-day finances by offering you personalized and timely information based upon your spending and saving routines by:
- Summarizing your daily financial transactions throughout all your accounts, including credit cards. NOMI knows when the deposit you made the other day is received or if your hydro bill is more than usual in a specific month.
- Telling you when there has been an uncommon or new activity. Remember that gym subscription auto-renewal you registered for? Well NOMI knows that, and will even tell you if they’ve raised your charges this year.
- Classifying your spending, with deep dives and easy-to-understand summaries to help you stay on the right financial track.
NOMI Find & Save can even set cash apart automatically to help you build up your emergency fund faster.
Money saving apps Canada: Scotiabank Bank the Rest
The third money saving apps Canada comes from Scotiabank (BNS). BNS has a savings program called Bank The Rest tied into any spending you do with your BNS debit card. It rounds up your purchases to your choice of either the closest $1 or $5. The additional amount is automatically moved to a Bank of Nova Scotia savings account for you.
This is a fun method of saving and is a clever way for this application to save you cash. Your purchases are assembled to the nearest multiple of 1 or 5. This allows you to bank extra funds due to the rounding up. If you purchase something for $6.45, you’ll bank $0.55 if you assemble to the nearest buck. Assemble to the nearest multiple of 5 (to $10 in this case), and you’ll bank $3.55. That’s a better and faster way for automatic savings from your spending.
Note that it is only for purchases on your BNS debit card, and not a credit card. This is a very smart thing. That way, the debit card, being just like cash, forces you to budget your cash spending and then makes an automatic savings program for you. This too will certainly help you build up that emergency savings fund. For this reason I call it the smartest of the money saving apps Canada in this list.
Money saving apps Canada: TD Canada Trust Track My Spend
The last in my list of money saving apps Canada is called Track My Spend. TD Canada Trust (TD) has developed an application that I believe will certainly be able to help you in keeping your budget plan. The app is called Track My Spend. Once activated, this app allows you to:
- Attach to your eligible TD Accounts. TD instantly tracks your transactions and classifies them for you. No need to go into it to manually add expenses or link your TD Accounts. It will do it automatically for you.
- Utilize the Spending Insights Meter to aid you to track how you’re doing compared to your common month-to-month spend. You will have the ability to get access to your Spending History (about the previous 12 months), so you can see precisely where your funds went.
- Help control your spending by setting regular monthly group targets and attempt to not surpass them. Additionally, you can split a single transaction into greater than one group.
- Get real-time notifications every time there’s a transaction in an eligible group, and assess your spending from the previous day with daily digest alerts. That way, you can keep an eye on your spending.
Although this app doesn’t automatically set money aside in an investment account, similar to Koho, it will change your spending patterns to allow you to save for that emergency fund.
Do you need more than just an app on your phone to deal with your debts?
Are you captured in the trap of excessive debt and only making minimal regular monthly repayments? Do you need more than just money saving apps Canada? Are you worried that future rates of interest increases will make currently affordable debt repayments entirely unaffordable? Is the stress, anxiety, and discomfort of your debt negatively influencing your health and wellness? Do you need a fresh kick-start and you don’t know where to begin? Do you believe that you need more than just an app on your phone?
If so, call the Ira Smith Team today. We have decades and generations of experience helping people and companies requiring financial restructuring. As a licensed insolvency trustee, we are the only professionals licensed and overseen by the Federal government to supply financial restructuring solutions.
Call the Ira Smith Team today to make sure that we can start assisting you. We will quickly return you right into a healthy and well-balanced stress-free life. We can create a debt settlement plan just for you to avoid bankruptcy, where we can even make the interest clock stop. This way, all your payments go only against the principal balances owing.
You can have a no-cost appointment to help you to fix your loan troubles. We recognize the pain financial debts and economic distress causes. We can end it from your life. This will absolutely allow you to start a fresh start, Starting Over Starting Now.
[monkeytools msnip=”http://monkeyplayr.com/playr.php?u=5173&p=20383″]