THIS IS OUR LAST BLOG FOR 2025. WE WILL RESUME IN MID-JANUARY 2026. MERRY CHRISTMAS AND HAPPY NEW YEAR TO ALL OUR FAITHFUL READERS AND OUR COMMUNITY.
DTI Key Takeaways
- Paradoxical Q2 and Q3 2025: Statistics Canada’s December 11, 2025, release reveals a confusing economic picture for Q2 and Q3 2025: a contracting national economy alongside a significant rise in household net worth.
- Market-Driven Wealth: The increase in household net worth is largely attributed to strong equity market performance, creating “paper wealth” through asset appreciation, rather than widespread income growth. This wealth is often concentrated.
- Rising DTI (Debt-to-Income Ratio): Despite increased net worth, Canadian households saw their aggregate DTI climb, indicating that debt is growing faster than income. A higher DTI signals increased financial fragility.
- Dipping Savings Rates: Concurrently, household saving rates declined, reducing the financial buffer available for emergencies or future investments and highlighting a reliance on borrowing.
- Implications for Consumers (2026): Canadians face a precarious balance. Prudent personal finance, debt reduction, and building emergency funds become critical. The lending landscape may tighten as a result of elevated DTI.
- Challenges for Businesses (2026): Entrepreneurs and companies must navigate shifting consumer spending power, potentially tighter access to capital, and adapt business models to focus on value and essential services in a more cautious economic climate.
- Strategic Caution: The overall message for 2026 is one of vigilance. While headline net worth looks robust, the underlying metrics, DTI and savings suggest a need for strategic planning, financial resilience, and prudent decision-making across all sectors.
According to Statistics Canada, household debt levels climbed again in the third quarter of 2025. The numbers show that for every dollar of disposable income Canadians earned, they carried about $1.77 in mortgages, credit cards, and other loans. Put simply, debt is now almost twice as large as the income households have available to spend or save.
Introduction: The Paradox at the Heart of the Canadian Economy
Imagine a situation where the national economy is shrinking, yet the financial worth of its citizens is on the rise. Sounds contradictory, doesn’t it? This is precisely the surprising headline expected from Statistics Canada’s December 11, 2025 release, detailing the National balance sheet and financial flow accounts for the second quarter of 2025. The report is set to reveal a significant increase in Canadian household net worth, painting a seemingly rosy picture of financial health.
However, beneath this surface glow, deeper metrics tell a more cautious story. The same report is anticipated to highlight less optimistic trends: a notable increase in household DTI (debt-to-income) ratios and a dip in saving rates. This immediate contradiction begs the question: how can Canadians be getting “richer” on paper while simultaneously taking on more debt and saving less?
This Brandon’s Blog post will dive deep into these figures, dissecting the StatsCan report to unpack what these seemingly conflicting trends truly mean. We’ll explore the drivers behind the surge in net worth, shine a critical light on the often-overlooked implications of a rising DTI, and understand why a falling saving rate is a cause for concern. More importantly, we’ll draw crucial conclusions, offering actionable insights for Canadian consumers, entrepreneurs, and companies as they navigate the complexities of 2026. This is essential reading for anyone with a stake in Canada’s economic future, seeking clarity amidst the paradox.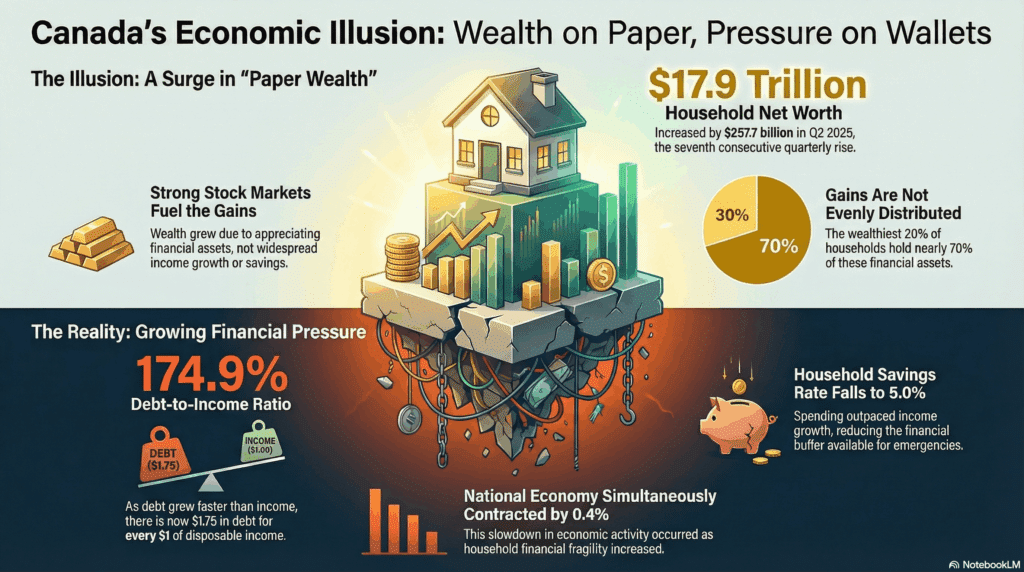
The Numbers Speak: Canada’s Q3 2025 Financial Snapshot (StatsCan December 11, 2025 Release)
The National balance sheet and financial flow accounts, released quarterly by Statistics Canada, are far more than just a collection of dry figures. They serve as a vital economic barometer, providing a comprehensive look at the financial health of Canadian households, non-profit organizations, corporations, and governments. By tracking assets, liabilities, and financial transactions, these reports offer invaluable insights into wealth accumulation, borrowing patterns, and investment behaviour – essentially, the financial pulse of the nation. The December 11, 2025, release is particularly noteworthy for its contradictory findings.
A Tale of Two Economies: National Contraction vs. Household Gains
The overarching narrative from the report will point to a contracting national economy. This typically signifies a slowdown in overall economic activity, often characterized by reduced GDP growth, potentially softer job markets, and a general tightening of economic conditions across various sectors. Such a contraction usually triggers concerns about recessionary pressures and the broader economic outlook.
Yet, in stark contrast to this contracting national picture, the report details an increase in aggregate household net worth. This figure, representing the total value of assets owned by households minus their liabilities (debts), can initially generate a sense of optimism. On the surface, it suggests Canadians are financially stronger, seemingly defying the broader economic headwinds. This immediate juxtaposition is where the core paradox lies, and it demands a closer, more nuanced examination to understand the true state of Canadian financial well-being.
Key Highlights from the National Balance Sheet
The primary driver behind the reported increase in household net worth is market-driven asset appreciation. This typically refers to the rising value of investments such as stocks, mutual funds, and other financial instruments held by households. When equity markets perform strongly, the value of these assets increases, directly boosting household net worth on paper, even if no new savings or income have been added. Other notable figures from the release, which we’ll delve into shortly, include the concerning trends of rising household DTI ratios and a dip in personal saving rates, setting the stage for a deeper analysis beyond the headline net worth figure.
Unpacking the Household Net Worth Surge: A Closer Look
While a rising household net worth sounds universally positive, it’s crucial to look beyond the surface number. “Household net worth” is a broad measure, and its increase doesn’t always translate directly into widespread, tangible prosperity for all Canadians. Understanding its composition and distribution is key to interpreting its true meaning.
The Equity Market Engine: Driving “Paper Wealth”
The primary engine behind the net worth surge is anticipated to be the strong performance of equity markets. This means that investments in stocks, mutual funds, and other market-linked assets have seen significant value appreciation. For households holding these assets, their wealth has increased on paper. This phenomenon is often referred to as “paper wealth” because it represents unrealized gains – the wealth exists as long as market valuations hold, but it hasn’t been converted into cash until assets are sold.
This market-driven appreciation can lead to what economists call the “wealth effect.” When people see their investment portfolios or home values rise, they often feel richer and more confident about their financial situation. This increased confidence can, in turn, lead to greater spending, despite their actual disposable income not having changed. While the wealth effect can stimulate economic activity, its foundations are often tied to market sentiment and performance, which can be volatile.
A critical point here is the concentration of this wealth. Equity market gains disproportionately benefit higher-income households, who typically hold a larger share of financial assets and investments. For many middle and lower-income Canadians, whose primary assets might be their home or defined-benefit pensions, the immediate impact of surging stock markets on their daily financial reality can be minimal. This means that while aggregate net worth rises, the benefits may not be evenly distributed, potentially widening the wealth gap rather than reflecting broad-based prosperity.
Beyond the Headlines: Is This Wealth Sustainable?
The reliance on market performance to drive net worth raises critical questions about its sustainability, especially within the context of a contracting national economy. If the increase in net worth is predominantly a function of rising asset prices rather than fundamental economic growth, real wage increases, or increased savings, its stability could be precarious.
Consider the potential vulnerabilities:
- Market Corrections: Equity markets are inherently cyclical. What goes up can come down. A significant market correction could quickly erode these “paper gains,” potentially leading to a rapid decline in household net worth.
- Economic Disconnect: When financial markets surge while the real economy (measured by GDP, employment, and business activity) contracts, it suggests a disconnect. This divergence can signal an economy propped up by financial speculation rather than robust underlying fundamentals.
- Interest Rate Sensitivity: The current interest rate environment plays a significant role. If rates continue to rise, it could put downward pressure on asset valuations (as higher rates typically reduce the present value of future earnings) and make borrowing more expensive, impacting both asset values and debt servicing costs.
For households with significant exposure to equities, while their net worth may look impressive on paper, they could be vulnerable to sudden shifts in market sentiment. This situation underscores the importance of a diversified financial strategy and a clear understanding that not all wealth is created equal, particularly when juxtaposed against other concerning financial indicators.
The Elephant in the Room: Canada’s Rising DTI and Dipping Savings
While the headline net worth figures might offer a fleeting sense of comfort, the StatsCan report’s deeper dive into household finances reveals a counter-narrative that demands serious attention: increasing DTI, ratios and declining saving rates. These are the less glamorous, but ultimately more telling, indicators of financial stability.
What is DTI, and Why is it Critically Important for Canadians?
The DTI is a financial metric that stands for Debt-to-Income Ratio. In simple terms, it compares how much money a person or household owes in debt payments each month to how much gross income they earn each month. It’s usually expressed as a percentage.
How is DTI calculated?
- Total Monthly Debt Payments: This includes all recurring debt obligations such as mortgage payments (principal and interest), car loans, student loan payments, minimum credit card payments, and any other regular loan payments.
- Gross Monthly Income: This is the total income before taxes and other deductions.
Formula: (Total Monthly Debt Payments / Gross Monthly Income) x 100 = DTI (%)
Why DTI Matters:
The DTI is a critical indicator for several reasons:
- Financial Health: A high DTI suggests that a large portion of one’s income is already committed to debt servicing. This leaves less money for essential living expenses, savings, or discretionary spending, making a household financially vulnerable.
- Creditworthiness: Lenders use DTI as a key factor in assessing credit risk. A lower DTI indicates that a borrower has more disposable income to manage new debt, making them a more attractive candidate for loans and mortgages.
- Ability to Absorb Shocks: Households with a high DTI have less flexibility to absorb unexpected financial shocks, such as job loss, illness, or sudden large expenses. They have little room to manoeuvre if their income decreases or their expenses rise.
- Lending Decisions: Most lenders have strict DTI limits. For instance, mortgage lenders often look for a total DTI (including the new mortgage payment) of no more than 40-44%. If a borrower’s DTI is too high, they may be denied credit or offered less favourable terms.
Healthy vs. Unhealthy DTI:
While benchmarks can vary by lender and financial institution, a general guide is:
DTI Range | Interpretation |
|---|---|
Below 36% | Excellent: Manageable debt, strong financial health. Ideal for lenders. |
36% – 43% | Good: Generally acceptable, but approaching limits for some loans. |
44% – 50% | Risky: May face challenges qualifying for new loans; high financial burden. |
Above 50% | Critical: Significant debt burden, very limited financial flexibility. |
Understanding your personal DTI is a foundational step towards managing your financial well-being.
Canadian DTI Trends: A Historical Context and Q2 and Q3 2025 Update
Canadian households have a long history of accumulating debt, particularly mortgage debt, due to rising housing prices. Over the past few decades, the aggregate household DTI has generally been on an upward trajectory, interrupted only by brief periods of deleveraging or economic slowdowns. Concerns about elevated household debt levels have been a recurring theme for economists and policymakers for years.
The Q3 2025 StatsCan report confirms a further increase in the aggregate household DTI ratio to almost 177%. The trend suggests that household debt is growing at a faster pace than disposable income. This upward movement is particularly concerning when juxtaposed with a contracting national economy, as it implies households are becoming more reliant on borrowing even as economic conditions weaken.
Several factors contribute to this rise:
- Persistent Inflation and Cost of Living: Even with a contracting economy, persistent inflation in essential goods and services (groceries, utilities) can push households to borrow more to maintain their standard of living.
- Higher Interest Rate Environment: While interest rates directly impact debt servicing costs, the aggregate DTI measures the ratio of debt payments to income. If rates rise, the payment portion of the DTI increases, even if the principal debt amount remains constant or grows slowly. This makes existing debt more expensive to carry, consuming a larger share of income.
- Consumption Patterns: Despite economic uncertainties, some households may continue pre-pandemic consumption patterns, funded through credit, or face unavoidable expenses that necessitate borrowing.
- Housing Market Dynamics: While the pace might have slowed, the high cost of housing and related borrowing continue to be a significant driver of overall household debt.
A rising DTI makes the Canadian financial system more vulnerable. It means that more households are stretched thin, with less capacity to manage financial shocks or unexpected expenses.
The Savings Squeeze: Living for Today, Borrowing for Tomorrow?
Adding to the complexity, the StatsCan report also details a dip in the household saving rate. The saving rate measures the proportion of disposable income that households save, rather than spend or use to pay down debt.
The implications of lower savings are significant:
- Reduced Financial Resilience: Savings act as a crucial buffer against unforeseen events like job loss, medical emergencies, or home repairs. A lower saving rate means households have less of a safety net, making them more susceptible to financial distress.
- Impaired Retirement Planning: Consistent savings are fundamental for long-term financial goals, including retirement. A sustained dip in saving rates can compromise future financial security for many Canadians.
- Limited Investment Capacity: Lower savings mean less capital available for personal investments, which can contribute to wealth building and economic growth.
Several factors could be contributing to this savings squeeze:
- Inflationary Pressures: The rising cost of living compels households to allocate a larger portion of their income to essential expenses, leaving less for savings.
- Higher Debt Servicing Costs: As interest rates rise and DTI increases, a greater share of income must be dedicated to servicing existing debt, directly reducing the amount available for saving.
- Post-Pandemic Spending: After periods of restricted spending during the pandemic, some households might have increased consumption, drawing down accumulated savings or delaying new savings.
- Income Stagnation: If real incomes are not keeping pace with inflation and rising expenses, households may find it increasingly difficult to save.
Taken together, the rising DTI and dipping saving rates paint a picture of Canadian households becoming more leveraged and less resilient, despite the headline boost in net worth. This situation poses a considerable challenge for individuals, businesses, and policymakers alike as they look towards 2026.
Reconciling the Paradox: Wealth on Paper, Pressure on Wallets
The Q3 2025 StatsCan report presents a challenging puzzle: how can Canada’s household net worth increase significantly while the national economy contracts, and individual households face rising DTI and falling savings? Reconciling these seemingly contradictory data points is crucial to understanding the true state of Canada’s economic health.
The Disconnect: Market Performance vs. Underlying Economic Strength
The primary explanation for this paradox lies in the fundamental disconnect between financial market performance and underlying economic strength. Stock markets, which are a major driver of “paper wealth” through asset appreciation, can often operate independently of the real economy.
- Financial Markets as Forward-Looking: Equity markets are often forward-looking, anticipating future earnings and economic conditions. Sometimes, they can be fuelled by optimism, speculative activity, or the performance of a few dominant sectors, even if the broader economy is struggling.
- Real Economy lags: The “real economy” – measured by GDP, employment rates, wage growth, and business investment – often moves at a different pace. A contracting real economy indicates a slowdown in actual production, consumption, and job creation.
- Interest Rate Environment: Policy interest rates can also influence this divergence. Central bank actions, aimed at controlling inflation or stimulating growth, can have immediate impacts on financial asset valuations (e.g., lower rates making equities more attractive) while their effects on the broader economy take longer to materialize.
This divergence can create an illusion of widespread prosperity when, in reality, the gains are concentrated and potentially volatile. It means that the rising net worth might not be a robust indicator of broad-based economic health, but rather a reflection of specific financial market dynamics.
This phenomenon is often described as a “K-shaped economy” or “K-shaped recovery.” In a K-shaped scenario, different segments of the economy and population experience vastly different outcomes. Some groups (the upper arm of the ‘K’) thrive, often those with significant financial assets, benefiting from market booms. Meanwhile, others (the lower arm of the ‘K’) struggle, perhaps facing job losses, stagnant wages, or increased debt burdens. The StatsCan Q2 and Q3 2025 data strongly hints at such a K-shaped distribution, where the aggregate net worth rises due to gains at the top, while the average Canadian experiences increased financial pressure.
Who Benefits? Dissecting the Distribution of Wealth and Debt
The aggregate figures for net worth, DTIDTI, and savings often mask significant disparities among Canadian households. The benefits of rising net worth are rarely evenly distributed.
- Concentration of Wealth: As mentioned, those with substantial investments in stocks, mutual funds, and other financial assets are the primary beneficiaries of equity market booms. These tend to be higher-income households. For many middle- and lower-income families, their primary “wealth” is often tied up in their home, and they may have fewer liquid financial assets to benefit from market rallies.
- Uneven Distribution of Debt: Conversely, the burden of rising debt and high DTIDTI ratios often falls disproportionately on younger Canadians, first-time homebuyers, and lower-to-middle-income households. These groups may have taken on significant mortgage debt at high prices, carry higher-interest consumer debt, or have experienced less robust income growth.
- Home Equity vs. Liquid Wealth: A significant portion of Canadian household net worth is tied up in home equity. While a rising home value increases net worth on paper, this “wealth” is often illiquid – it can’t be easily accessed without selling the home or taking on more debt (e.g., through a home equity line of credit). This means that while net worth looks good, many households might not have readily accessible funds to cover emergencies or maintain their lifestyles without further borrowing. This lack of liquid wealth, coupled with increasing DTI, creates a vulnerable financial landscape for many.
In essence, the Q3 2025 report suggests a narrative where a segment of the population is enjoying market-driven wealth appreciation, while a broader swathe of Canadians is grappling with the pressures of rising debt and shrinking financial buffers. This divergence creates a complex and potentially fragile economic environment for 2026.
Implications for Canadian Consumers in 2026: Navigating the New Reality
For the average Canadian consumer, the mixed signals from the Q3 2025 StatsCan report demand careful consideration. Navigating 2026 will require a proactive and informed approach to personal finance.
Personal Finance Strategies: Budgeting, Debt Reduction, and Emergency Funds
In an environment characterized by a high aggregate DTIDTI and low saving rates, a robust personal finance strategy is no longer optional; it’s essential.
- Aggressive Debt Repayment: Prioritize paying down high-interest debt, such as credit card balances and personal lines of credit. Even if overall net worth is up, high-interest debt eats away at disposable income and financial flexibility. Consider strategies like the debt snowball or debt avalanche methods.
- Re-evaluating Budgets: With persistent inflation and potentially stagnant real incomes, a thorough review of household budgets is critical. Identify areas where expenses can be reduced to free up funds for debt repayment or savings. Differentiate between needs and wants.
- Prioritizing Emergency Savings: The dip in saving rates is a significant red flag. Aim to build or replenish an emergency fund covering at least three to six months of essential living expenses. This fund provides a crucial buffer against unexpected job loss, health issues, or other financial shocks.
- Understanding Your Own DTI: Every individual should know their personal DTI. Regularly calculate it to monitor your financial health. If it’s high, focus on increasing income or, more realistically, reducing debt payments. Tools like online calculators or financial advisors can help. A lower DTI improves credit scores and opens doors to better lending rates.
The Mortgage and Lending Landscape: What Rising DTI Means for Borrowers
The aggregate increase in household DTI will undoubtedly influence the mortgage and broader lending landscape in 2026. Lenders are inherently risk-averse, and a national trend of higher debt relative to income signals increased risk.
- Stricter Qualification Criteria: Banks and other financial institutions may tighten their lending criteria. This could mean higher minimum credit scores, more stringent income verification, and potentially lower maximum DTI thresholds for loan approvals, particularly for mortgages and large personal loans.
- Impact on First-Time Homebuyers: For those looking to enter the housing market, a higher national DTI could make it more challenging to qualify for mortgages, especially if interest rates remain elevated. They might need larger down payments or demonstrate exceptionally strong income stability.
- Refinancing Challenges: Existing homeowners looking to refinance their mortgages or access home equity lines of credit might also face stricter scrutiny. Their current DTI will be a significant factor, and higher rates could make refinancing less attractive or even unfeasible.
- Increased Scrutiny on Debt Servicing: Lenders will place an even greater emphasis on an applicant’s ability to service existing debt, making a clean credit history and a manageable DTI more important than ever.
Consumer Confidence and Spending Habits: A Precarious Balance
The mixed economic signals create a precarious balance for consumer confidence and, consequently, spending habits.
- Cautious Spending: While some may feel wealthier due to asset appreciation, the underlying pressures of high DTI and low savings are likely to foster a more cautious mindset among the majority of consumers. This could lead to a reduction in discretionary spending on non-essential goods and services.
- Shift Towards Value: Consumers may increasingly seek out value-oriented products and services, prioritizing necessity over luxury. Bargain hunting, sales, and a focus on durability are likely to become more prevalent.
- Impact on Certain Sectors: Sectors heavily reliant on discretionary spending (e.g., luxury retail, high-end travel, fine dining) could experience a slowdown, while essential services, discount retailers, and financial advisory services (especially those focused on debt management) might see increased demand.
- Economic Uncertainty: The contracting national economy, coupled with global uncertainties, will likely keep consumer confidence subdued, leading to a “wait-and-see” approach for major purchases or investments.
For Canadian consumers, 2026 will be a year to embrace financial prudence, resilience, and strategic planning.
What This Means for Canadian Entrepreneurs and SMEs in 2026
Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) are the backbone of the Canadian economy, and they will feel the ripple effects of these complex financial trends directly. Entrepreneurs must be agile and strategic to thrive in 2026.
Understanding Consumer Spending Power and Risk Appetite
Entrepreneurs need to keenly interpret the nuanced consumer data revealed by StatsCan to inform their business planning.
- Divergent Spending Patterns: Recognize that consumer spending power is likely to be uneven. While some higher-net-worth households may continue spending, a larger segment of consumers grappling with high DTI and low savings will be more cautious. Businesses should avoid assuming broad-based consumer affluence.
- Demand for Value and Essentials: Businesses that offer strong value propositions, essential goods and services, or solutions that help consumers manage their finances (e.g., budget-friendly alternatives, repair services over new purchases, financial planning) are likely to be more resilient.
- Reduced Discretionary Spending: Businesses in discretionary sectors will need to prepare for potentially reduced demand. This might necessitate marketing shifts, product line adjustments, or a renewed focus on customer retention through exceptional service.
- Reluctance to Take on New Debt for Purchases: Consumers with high personal DTI are less likely to finance large purchases or take on new credit for non-essential items, directly impacting businesses selling big-ticket goods or services.
Access to Capital and Lending Conditions for Businesses
The elevated aggregate household DTI and broader economic contraction can influence the lending environment for SMEs.
- Tighter Credit Conditions: Financial institutions, facing increased systemic risk from household debt, may become more cautious in their lending to businesses as well. This could mean higher interest rates, stricter collateral requirements, or more rigorous financial scrutiny for SME loan applications.
- Emphasis on Strong Financials: Entrepreneurs seeking capital will need to present an even stronger case, demonstrating robust cash flow, a solid business plan, a clear path to profitability, and potentially more personal capital injection to de-risk the loan.
- Alternative Financing: SMEs might need to explore alternative financing options beyond traditional bank loans, such as government grants, venture capital (for scalable businesses), or crowdfunding, though these also come with their own sets of challenges and requirements.
- Managing Existing Debt: Businesses with existing debt should review their terms and proactively manage their obligations, especially if interest rates continue to climb. Strong cash flow management becomes paramount.
Opportunity in Uncertainty: Adapting Business Models
Despite the challenges, periods of economic uncertainty can also create unique opportunities for adaptable and innovative entrepreneurs.
- Innovation in Value Delivery: Businesses that can innovate to provide more cost-effective solutions or higher perceived value for the consumer dollar will gain a competitive edge. This could involve process improvements, supply chain optimization, or creative pricing models.
- Focus on Essential Services: Expanding into or fortifying offerings in essential services, repair, maintenance, or financial advisory (e.g., budgeting tools, debt consolidation advice) can tap into resilient demand.
- Digital Transformation: Leveraging digital tools for efficiency, customer outreach, and e-commerce can help businesses reach a wider audience and reduce overhead, critical in a tighter economic climate.
- Niche Market Focus: Identifying and serving niche markets with specific, unmet needs (e.g., sustainable and affordable products, personalized services that save time or money) can provide resilience against broader economic downturns.
- Contingency Planning: Building robust financial models, establishing strong cash reserves, and developing clear contingency plans for various economic scenarios (e.g., reduced sales, supply chain disruptions) are vital for long-term survival.
Entrepreneurs in 2026 must lead with prudence, agility, and a deep understanding of evolving consumer behaviour and financial market realities.
Strategic Outlook for Canadian Companies in 2026
Larger Canadian companies, with broader market reach and significant investment capabilities, also face a complex landscape in 2026. Strategic decisions regarding investment, risk management, and workforce planning will be critical.
Investment Decisions and Capital Allocation
The contracting national economy, coupled with high household DTI will influence how companies approach investment and capital allocation.
- Cautious Expansion: Companies may adopt a more conservative approach to major capital expenditures, R&D, and expansion plans. Investment decisions will likely undergo heightened scrutiny, prioritizing projects with clear and immediate returns on investment.
- Focus on Efficiency: Investments aimed at improving operational efficiency, reducing costs, and streamlining processes will likely take precedence. This could involve adopting automation, optimizing supply chains, or investing in energy-saving technologies.
- Maintaining Liquidity: In an uncertain economic environment, maintaining strong liquidity and a healthy balance sheet will be paramount. Companies may choose to hoard cash or pay down existing debt rather than embarking on aggressive growth initiatives.
- Strategic M&A: Opportunistic mergers and acquisitions could occur, especially if smaller, less resilient businesses become available at attractive valuations. However, even these deals will face rigorous due diligence.
Managing Risk in a Fluctuating Economic Environment
The confluence of a contracting economy, elevated household DTI, and global uncertainties significantly raises the risk profile for Canadian companies.
- Credit Risk from Consumers: Companies that rely on consumer credit or offer financing (e.g., automotive, retail) will need to closely monitor their credit risk exposure, as a higher aggregate DTI suggests an increased likelihood of defaults or delayed payments.
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: Ongoing geopolitical tensions and potential disruptions can continue to pose risks to global supply chains. Companies should invest in diversification, resilience planning, and near-shoring strategies where feasible.
- Market Volatility: The market-driven nature of net worth gains suggests financial markets could remain volatile. Companies with significant financial investments or pension liabilities will need robust hedging strategies.
- Forecasting Challenges: Economic forecasting becomes more challenging in a mixed-signal environment. Companies need dynamic forecasting models and adaptable strategies to respond to rapidly changing market conditions.
- Cybersecurity Risks: As economic pressures mount, cybersecurity threats can also increase, requiring continuous investment in robust protective measures.
Workforce Planning and Consumer Demand Shifts
Changes in consumer spending patterns and a potential economic slowdown will have direct implications for workforce planning and human resources.
- Moderated Hiring: Companies may slow the pace of hiring or implement targeted hiring freezes, especially in sectors experiencing reduced consumer demand. Growth in employment might be modest.
- Talent Retention: Despite potential slowdowns, retaining key talent will remain crucial. Companies might focus on non-monetary benefits, professional development, and fostering a positive work environment to maintain their workforce.
- Skill Gaps: The need for efficiency and digital transformation could lead to shifts in required skills, necessitating investments in reskilling and upskilling programs for the existing workforce.
- Impact on Different Sectors: Companies in discretionary goods and services will likely face greater pressure on their workforce than those in essential services, healthcare, or utilities. Resource allocation and restructuring may be necessary in some sectors.
- Productivity Focus: With potential wage pressures and a cautious economic outlook, companies will increasingly focus on improving workforce productivity through technology, training, and optimized processes.
For Canadian corporations, 2026 calls for a strategic approach that balances prudent risk management with selective, high-impact investments, ensuring resilience and adaptability in a complex economic climate.
Preparing for 2026: Recommendations and Forward-Looking Strategies
The StatsCan report serves as a crucial wake-up call, emphasizing the need for proactive measures across all economic stakeholders. Preparing for 2026 requires a consolidated strategy focused on resilience, prudence, and informed decision-making.
For Individuals: Building Financial Resilience
- Debt Reduction Focus: Make aggressive repayment of high-interest debt a top financial priority. Understanding your personal DTI is the first step towards improving it.
- Savings First: Recommit to consistent saving, even small amounts. Build an emergency fund and prioritize long-term financial goals like retirement, mitigating the impact of dipping national saving rates.
- Budget with Discipline: Create and adhere to a realistic budget that accounts for inflation and potential income fluctuations. Differentiate between needs and wants.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consult with financial advisors to review your personal financial plan, assess your risk tolerance, and optimize your investment and debt management strategies.
- Cautious Spending & Investing: Approach major purchases and investments with caution, conducting thorough due diligence and avoiding overleveraging.
For Businesses: Prudent Growth and Risk Management
- Optimize Operations & Cash Flow: Focus on improving operational efficiencies, managing costs, and strengthening cash flow. A strong balance sheet provides a critical buffer against economic headwinds.
- Understand Your Customer: Deeply analyze evolving consumer spending patterns and preferences. Adapt product offerings, marketing strategies, and value propositions to meet the needs of a more cautious consumer base.
- Diversify & Innovate: Explore new markets, diversify revenue streams, and innovate in product and service delivery. Seek out niches that cater to current economic realities.
- Proactive Capital Planning: If seeking financing, prepare comprehensive business plans and robust financial projections. Explore diverse funding sources beyond traditional lending.
- Talent Strategy: Focus on retaining key talent through engagement and development, while aligning workforce planning with anticipated demand.
Policy Considerations
- Fiscal Prudence: Governments may need to exercise fiscal prudence, balancing support for economic growth with managing public debt, especially if the private sector is deleveraging.
- Targeted Support: Policies aimed at easing the burden of high DTI for vulnerable households (e.g., debt counselling services, targeted affordability measures) could enhance financial stability.
- Market Oversight: Regulators may need to maintain vigilance over financial markets to prevent excessive speculation and ensure stability, given the market-driven nature of net worth increases.
- Productivity Enhancements: Policies that foster innovation, investment in technology, and skill development can help boost overall economic productivity, addressing underlying economic contraction.
- Housing Affordability: Continued focus on increasing housing supply and addressing affordability challenges can alleviate one of the major drivers of household debt.
Frequently Asked Questions About the Debt-to-Income Ratio ([DTI])
Understanding your Debt-to-Income Ratio ([DTI]) is a foundational step in managing your financial well-being. This financial metric is becoming increasingly important as Canadian households navigate complex economic signals.
DTI Most Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What exactly is the Debt-to-Income Ratio (DTI)?
The Debt-to-Income Ratio, commonly called DTI, is a key financial metric that measures the proportion of your income that is committed to paying off debt each month. It compares how much money a person or household pays towards debt obligations monthly against the total gross income (income before taxes) they earn each month. A higher DTI tells economists that debt is increasing faster than income, suggesting that households are becoming financially fragile.
2. How is my personal DTI calculated?
The DTI is calculated by following a straightforward formula:
(Total Monthly Debt Payments / Gross Monthly Income) x 100 = DTI (%)
“Total Monthly Debt Payments” includes all regular debt obligations, such as minimum credit card payments, car loans, student loan payments, and mortgage payments (principal and interest). Lenders focus on your DTI because a lower ratio indicates that you have more disposable income available to manage any new debt, making you a more appealing candidate for loans and mortgages.
3. What is considered a healthy versus a high DTI?
Benchmarks for a healthy DTI can vary, but generally, having a manageable debt level is critical for financial health. A high DTI means that a large portion of your income is already dedicated to servicing debt, leaving less money for things like discretionary spending, savings, or essential living costs.
Here is a general guide to interpreting DTI ranges:
• Below 36%: This is considered Excellent and is ideal for lenders, suggesting manageable debt and strong financial health.
• 44% – 50%: This range is Risky, indicating a high financial burden where you may face difficulties qualifying for new loans.
• Above 50%: This is Critical, representing a significant debt burden and extremely limited financial flexibility.
Households with a high DTI have less ability to cope with unexpected financial challenges, such as a major expense or job loss.
4. What is the current aggregate DTI for Canadian households?
Canadian households have historically taken on significant debt, especially mortgage debt. Recent data confirms that the aggregate household DTI has continued to climb, suggesting that debt is outpacing disposable income.
For the second quarter of 2025, the ratio of household credit market debt as a proportion of household disposable income was 174.9%. This means that for every dollar of household disposable income, Canadians held $1.75 in credit market debt. Furthermore, reports for the third quarter of 2025 suggested a further increase in the aggregate ratio to almost 177%.
5. How does a rising national DTI affect my ability to borrow money in 2026?
A high national DTI signals increased risk across the financial system. Since lenders are cautious, this trend will likely influence the lending environment in 2026.
Specifically, you may encounter:
• Stricter Rules: Financial institutions may tighten their lending standards, potentially requiring higher minimum credit scores and lowering the maximum DTI thresholds they will accept for large loans and mortgages.
• Increased Difficulty: If you are a first-time homebuyer or seeking to refinance, the elevated national DTI could make it harder to qualify for financing, especially if interest rates remain high.
• More Scrutiny: Lenders will focus even more intensely on your personal ability to service your existing debt.
For consumers, navigating 2026 successfully requires prudence, aggressive repayment of high-interest debt, and knowing—and ideally improving—your own personal DTI. This situation underscores why reducing debt and building emergency savings are crucial personal finance strategies.
Conclusion: Beyond the Numbers – A Call to Prudence
The December 11, 2025, Statistics Canada release presents Canada with a nuanced and challenging economic portrait. While the headline rise in household net worth might offer a superficial comfort, a deeper dive reveals a critical story of increasing DTI and dipping saving rates against a backdrop of a contracting national economy. This is not a broad-based economic triumph but rather a complex scenario where market-driven “paper wealth” coexists with growing financial pressure on many Canadian households.
The path ahead for 2026 is one that demands vigilance and strategic planning from all stakeholders. For individuals, it’s a call to strengthen personal financial resilience, prioritize debt reduction, and rebuild savings. For businesses, it’s an imperative to adapt, innovate, and manage risk with prudence and agility. For policymakers, it highlights the need for considered strategies that address both the symptoms and root causes of financial fragility.
Ultimately, while the numbers paint a complex picture, proactive planning, informed decision-making, and a balanced perspective of both opportunity and caution can help Canadians navigate 2026 successfully, fostering true, sustainable economic health rather than just an illusion of wealth.
Debt Relief Services Overview
Don’t let the burden of debt dictate your future for another day. A fresh start is not just a dream; it’s a legal reality available to you in Toronto, Vaughan, Woodbridge, Thornhill, Richmond Hill and all of the GTA. It is designed to help you regain control and peace of mind.
Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc. is here to help you navigate your options with unparalleled expertise, genuine empathy, and unwavering professionalism. As Licensed Insolvency Trustees, we are the only professionals authorized by the Canadian government to provide these powerful debt relief solutions. We understand the legal framework and how to apply it to your unique situation to achieve the best possible outcome.
Take the crucial first step towards your debt-free future today. You don’t have to carry this burden alone. Contact Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc. now for a FREE, no-obligation consultation. Let us help you find your clear path to a brighter, financially secure tomorrow. Your fresh start is waiting.
Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc. is licensed by the Office of the Superintendent of Bankruptcy and is a member of the Canadian Association of Insolvency and Restructuring Professionals.
Contact Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc. Today:
- Phone: 905.738.4167
- Toronto line: 647.799.3312
- Website: https://irasmithinc.com/
- Email: brandon@irasmithinc.com
——————————————————————————–
Disclaimer: This analysis is for educational purposes only and is based on the cited sources and my professional expertise as a licensed insolvency trustee. The information provided does not constitute legal or financial advice for your specific circumstances.
Every situation is unique and involves complex legal and factual considerations. The outcomes discussed in this article may not apply to your particular situation. Situations are fact-specific and depend on the particular circumstances of each case.
Please contact Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc. or consult with qualified legal or financial professionals regarding your specific matter before making any decisions.
About the Author:
Brandon Smith is a Senior Vice-President at Ira Smith Trustee & Receiver Inc. and a licensed insolvency trustee serving clients across Ontario. With extensive experience in complex court-ordered receivership administration and corporate insolvency & restructuring proceedings, Brandon helps businesses, creditors, and professionals navigate challenging financial situations to achieve optimal outcomes.
Brandon stays current with landmark developments in Canadian insolvency law. He brings this cutting-edge knowledge to every client engagement, ensuring his clients benefit from the most current understanding of their rights and options.